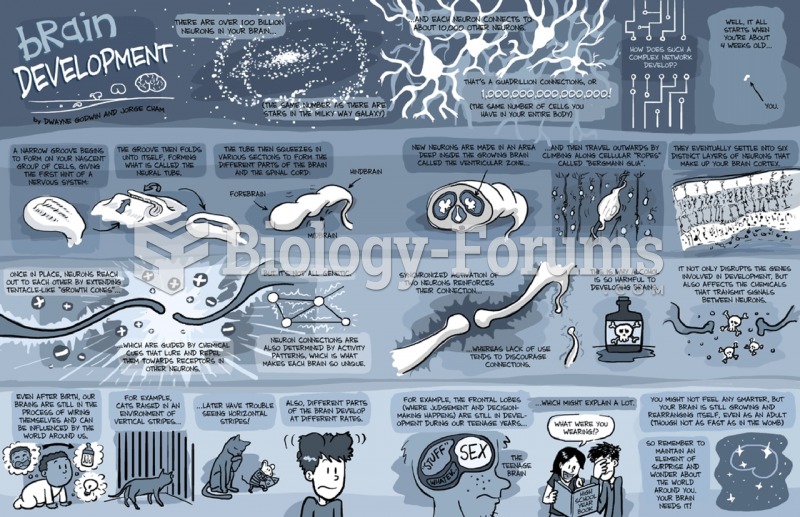
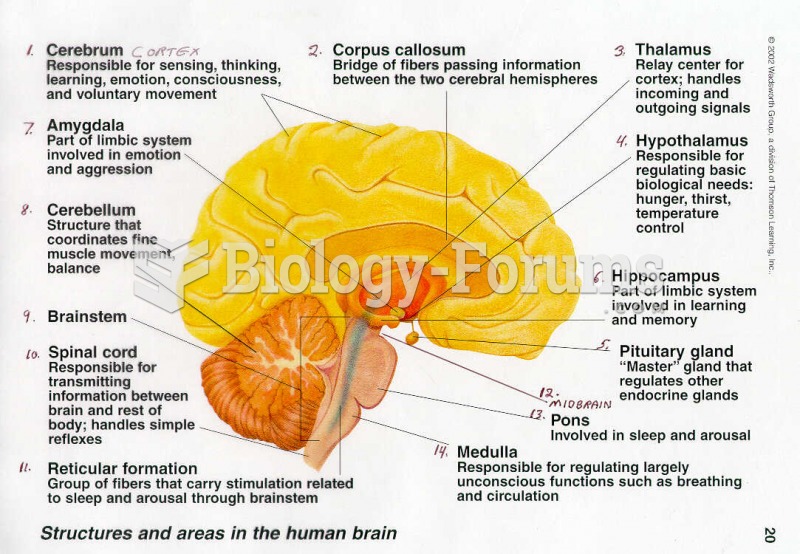
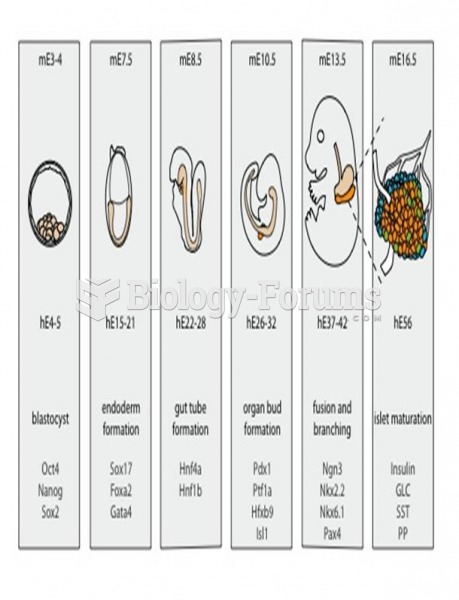
|
|
|
Did you know?
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.
Did you know?
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Did you know?
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Did you know?
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
Did you know?
After 5 years of being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, one every three patients will no longer be able to work.