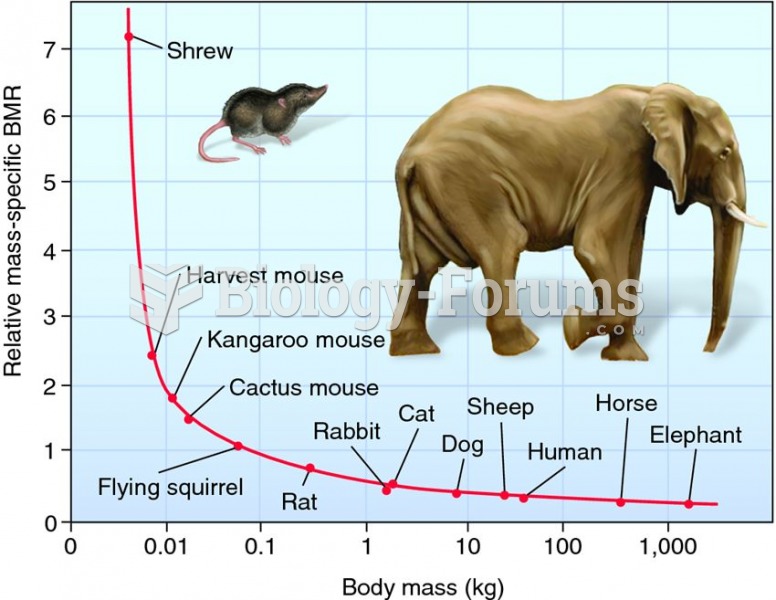
|
|
|
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.
To maintain good kidney function, you should drink at least 3 quarts of water daily. Water dilutes urine and helps prevent concentrations of salts and minerals that can lead to kidney stone formation. Chronic dehydration is a major contributor to the development of kidney stones.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
Approximately 500,000 babies are born each year in the United States to teenage mothers.
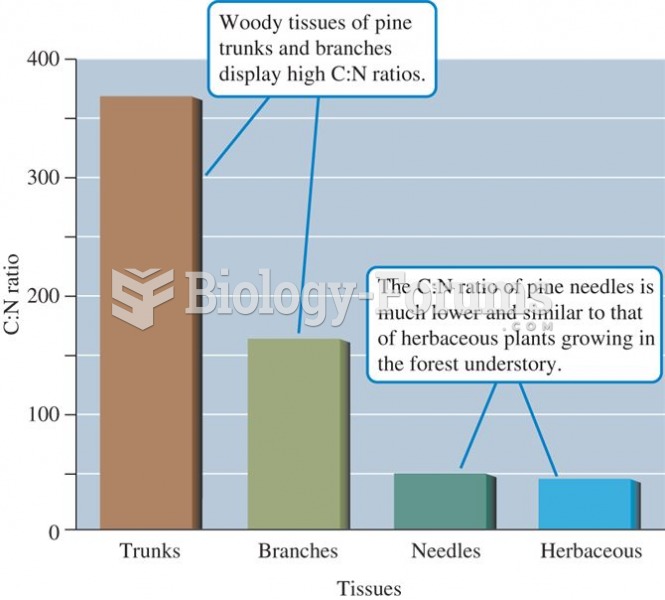 C:N ratios differ a great deal among the tissues of pines and between the woody tissues of pines and
C:N ratios differ a great deal among the tissues of pines and between the woody tissues of pines and
 Hong Kong is a strange situation. A British colony since 1842, it was handed back to China in 1997 a
Hong Kong is a strange situation. A British colony since 1842, it was handed back to China in 1997 a