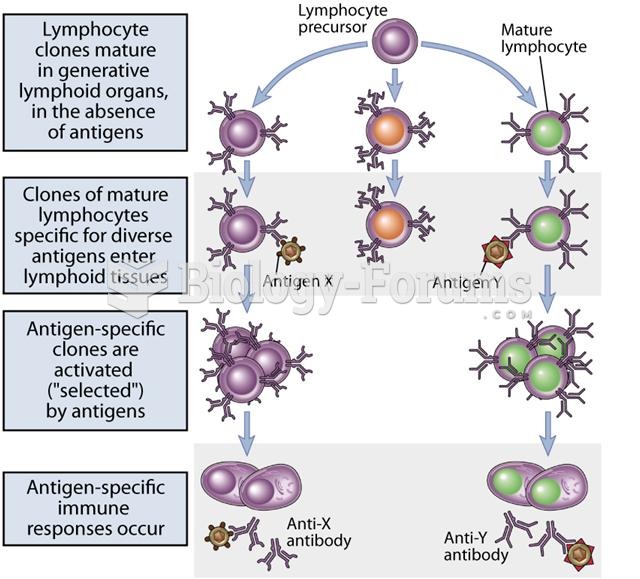
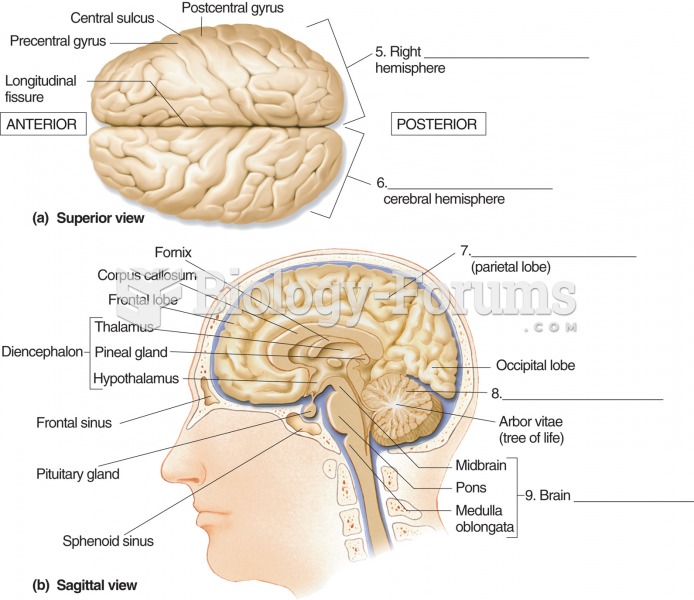
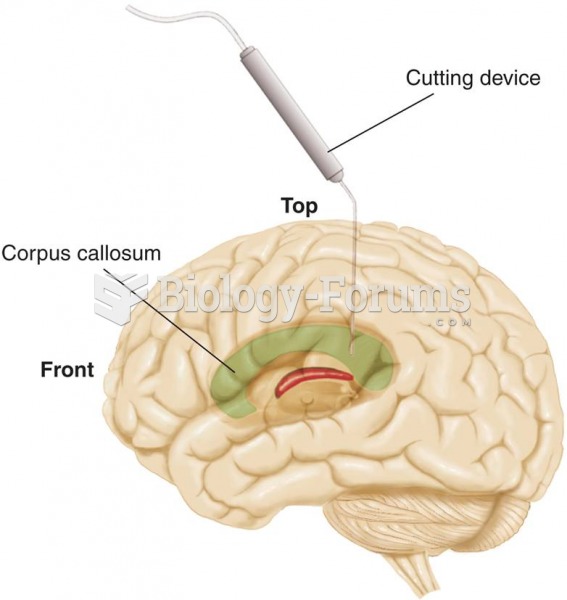
|
|
|
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.
The horizontal fraction bar was introduced by the Arabs.
Pope Sylvester II tried to introduce Arabic numbers into Europe between the years 999 and 1003, but their use did not catch on for a few more centuries, and Roman numerals continued to be the primary number system.