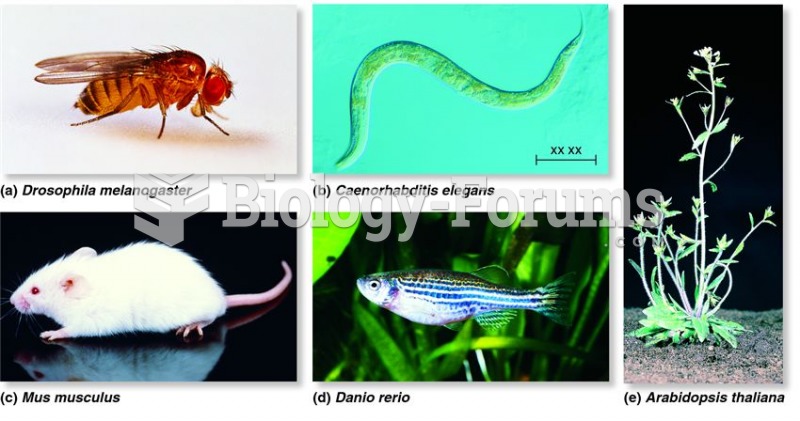
|
|
|
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.
It is believed that the Incas used anesthesia. Evidence supports the theory that shamans chewed cocoa leaves and drilled holes into the heads of patients (letting evil spirits escape), spitting into the wounds they made. The mixture of cocaine, saliva, and resin numbed the site enough to allow hours of drilling.
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.