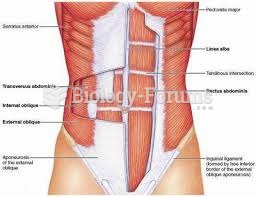
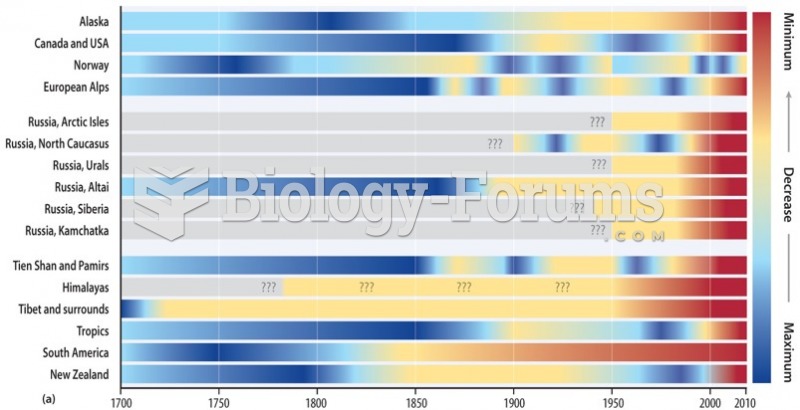
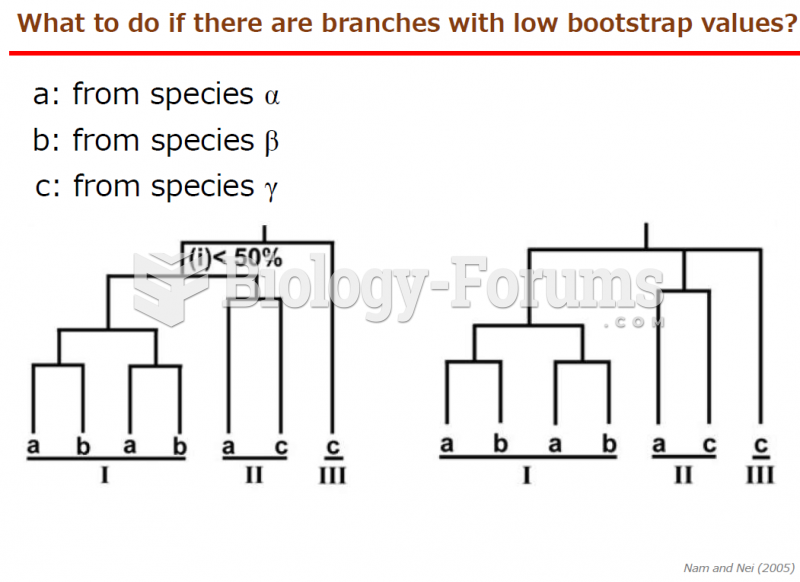
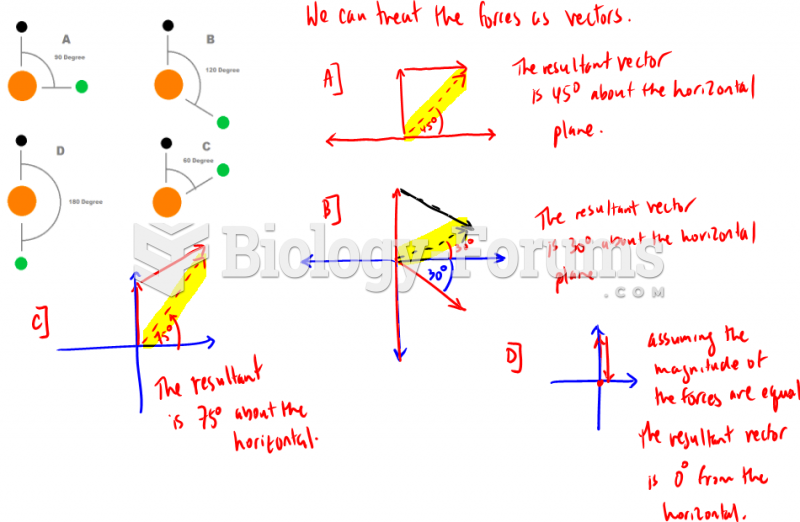
|
|
|
In 1844, Charles Goodyear obtained the first patent for a rubber condom.
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.
Studies show that systolic blood pressure can be significantly lowered by taking statins. In fact, the higher the patient's baseline blood pressure, the greater the effect of statins on his or her blood pressure.
Always store hazardous household chemicals in their original containers out of reach of children. These include bleach, paint, strippers and products containing turpentine, garden chemicals, oven cleaners, fondue fuels, nail polish, and nail polish remover.