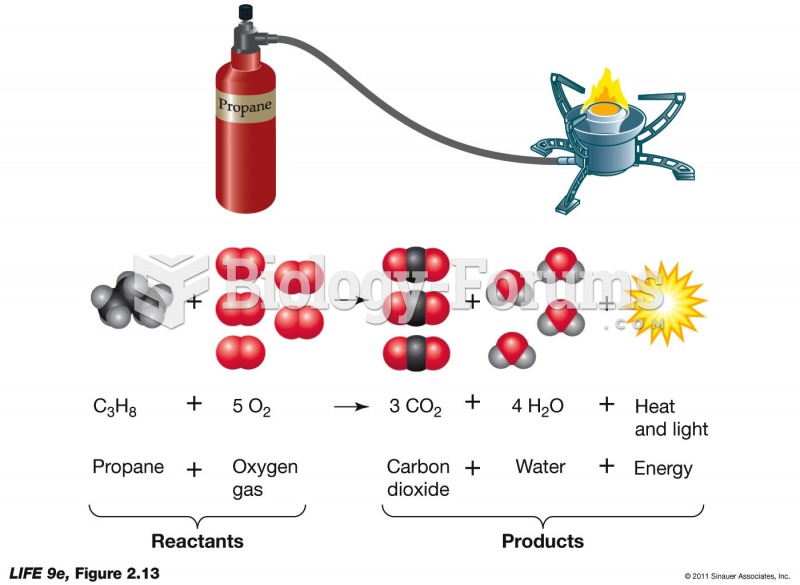
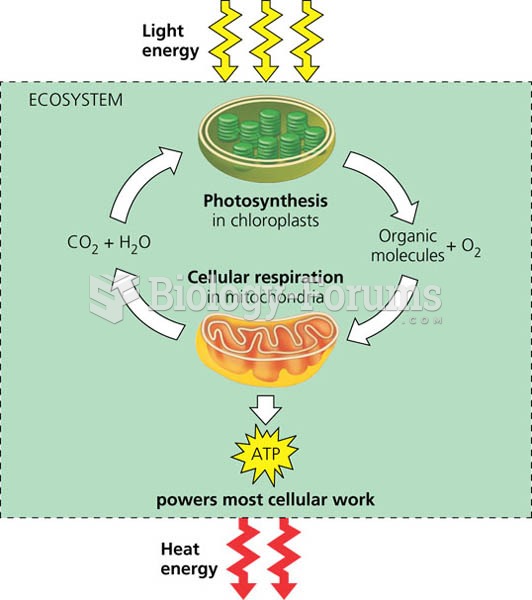
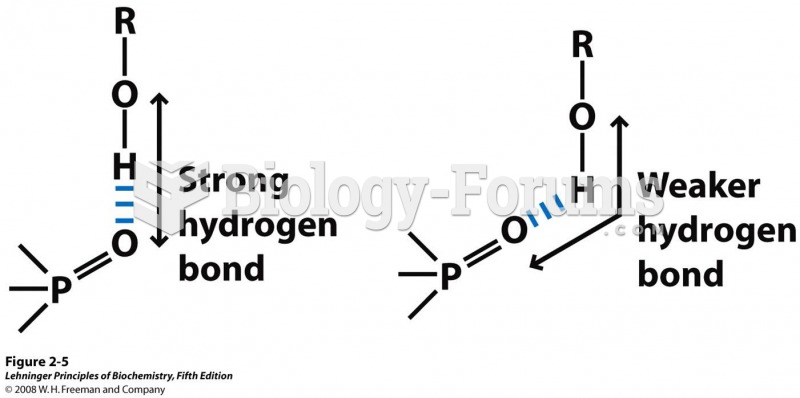
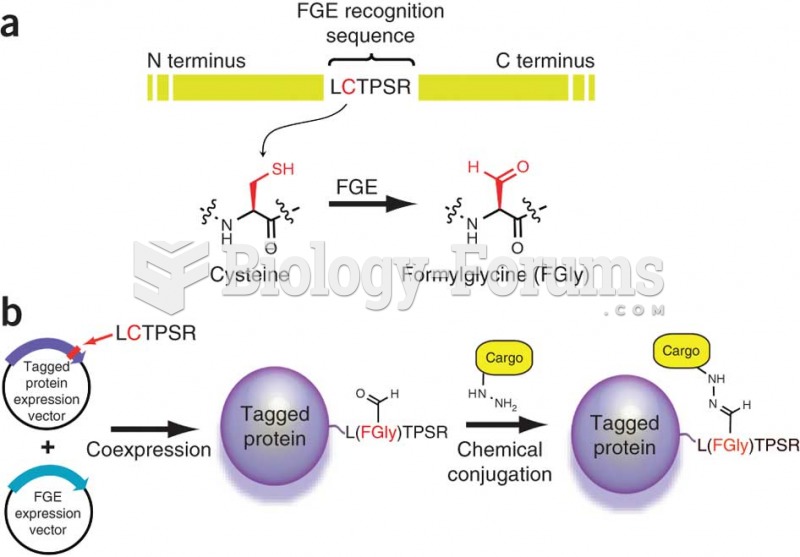
|
|
|
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%.
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
In the United States, an estimated 50 million unnecessary antibiotics are prescribed for viral respiratory infections.