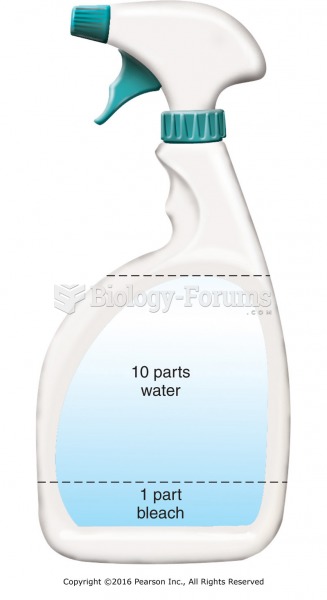
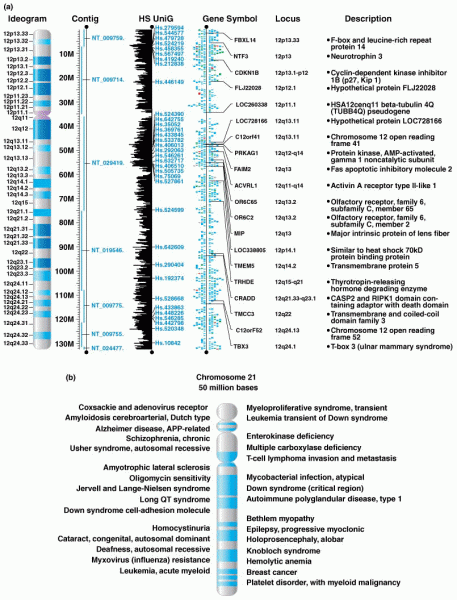
|
|
|
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Each year in the United States, there are approximately six million pregnancies. This means that at any one time, about 4% of women in the United States are pregnant.
Parkinson's disease is both chronic and progressive. This means that it persists over a long period of time and that its symptoms grow worse over time.
Drugs are in development that may cure asthma and hay fever once and for all. They target leukotrienes, which are known to cause tightening of the air passages in the lungs and increase mucus productions in nasal passages.
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.