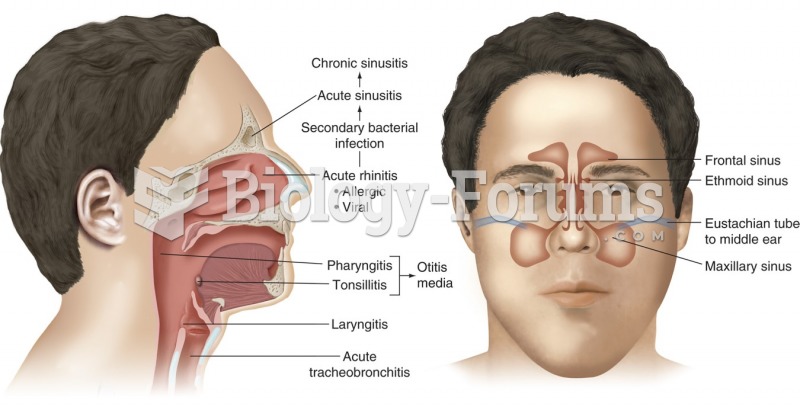
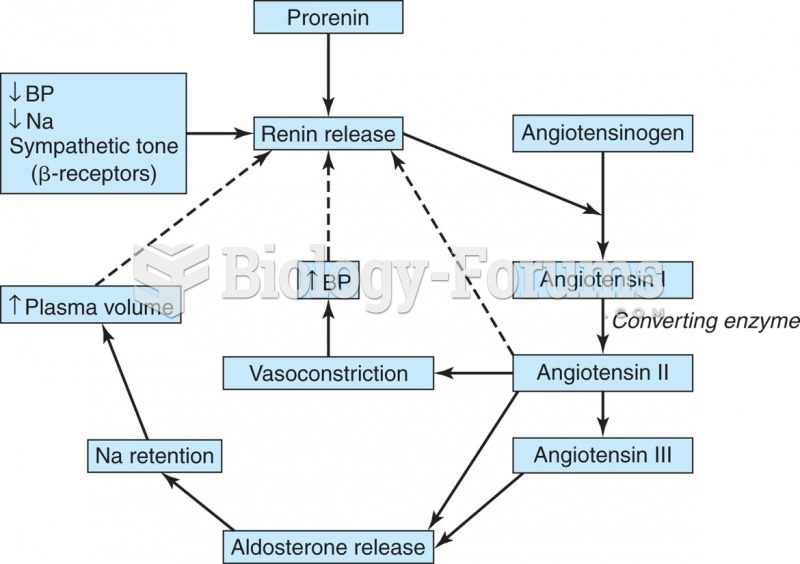
Answer to Question 1
The Treaty of Versailles grew out of a desire for retribution. In brief, Germany's
military was drastically cut; it was forbidden to possess heavy artillery, military
aircraft, or submarines, and its forces were banned from the Rhineland. Germany
also lost territory in the west to France and Belgium, in the south to the new state of
Czechoslovakia, and in the east to the new states of Poland and Lithuania. Overseas,
Germany lost all of its colonies. Finally, in the most humiliating clause of the treaty,
Germany was assigned responsibility for the war and charged with paying heavy
financial reparations for the damages. On learning of the treaty's harsh provisions, the
exiled German kaiser is said to have declared the war to end wars has resulted in a
peace to end peace.. Structural realism emphasizes polarity as a defining feature of
the international system and, at the global level of analysis, regards the reemergence
of multipolarity in global power distribution as a key factor in the onset of World War
II. The postWorld War I global system was precarious because the number of
sovereign states increased at the same time the number of great powers declined. In
1914, Europe had only 22 key states, but by 1921 the number had nearly doubled.
Resentment over the Versailles treaty, the Russian Revolution, and the rise of
fascism, the increased number of states and the resurgence of nationalistic revolts and
crises made war inevitable. The Cold War began to affect the trajectories of states
and political movements across the globe. Circumstances gave each superpower
reasons to fear and struggle against the other's potential global leadership, and
encouraged both competitors to carve out and establish a wide sphere of influence, or
specified areas of the globe.
Answer to Question 2
The Treaty of Versailles grew out of a desire for retribution. In brief, Germany's
military was drastically cut; it was forbidden to possess heavy artillery, military
aircraft, or submarines, and its forces were banned from the Rhineland. Germany
also lost territory in the west to France and Belgium, in the south to the new state of
Czechoslovakia, and in the east to the new states of Poland and Lithuania. Overseas,
Germany lost all of its colonies. Finally, in the most humiliating clause of the treaty,
Germany was assigned responsibility for the war and charged with paying heavy
financial reparations for the damages. On learning of the treaty's harsh provisions, the
exiled German kaiser is said to have declared the war to end wars has resulted in a
peace to end peace..