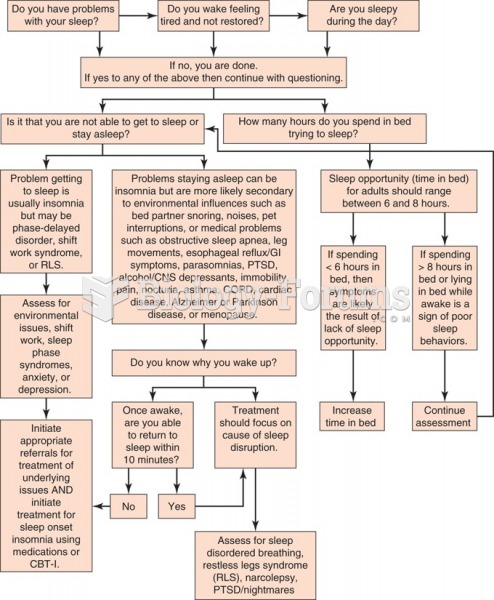
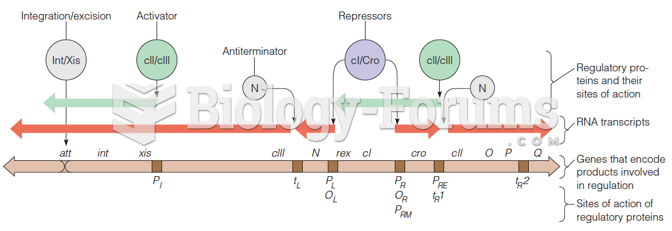
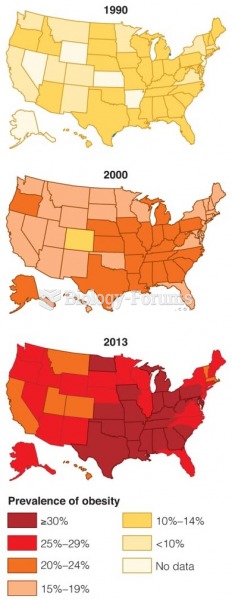
|
|
|
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
Side effects from substance abuse include nausea, dehydration, reduced productivitiy, and dependence. Though these effects usually worsen over time, the constant need for the substance often overcomes rational thinking.
As of mid-2016, 18.2 million people were receiving advanced retroviral therapy (ART) worldwide. This represents between 43–50% of the 34–39.8 million people living with HIV.
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. As of yet, there is no cure. Everyone is at risk, and there may be no warning signs. It is six to eight times more common in African Americans than in whites. The best and most effective way to detect glaucoma is to receive a dilated eye examination.