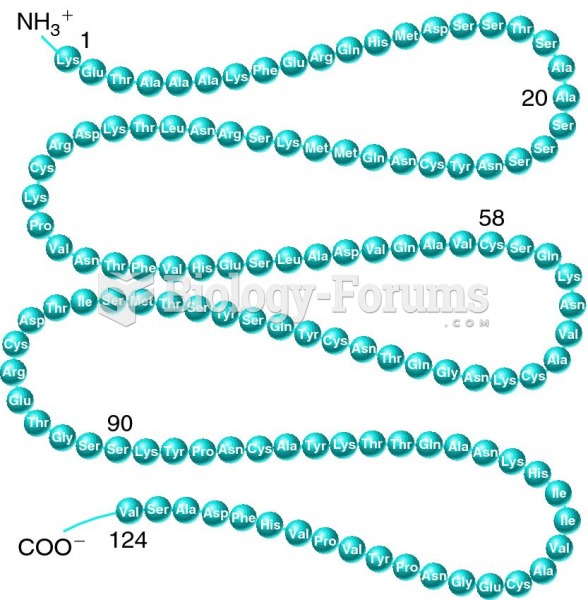
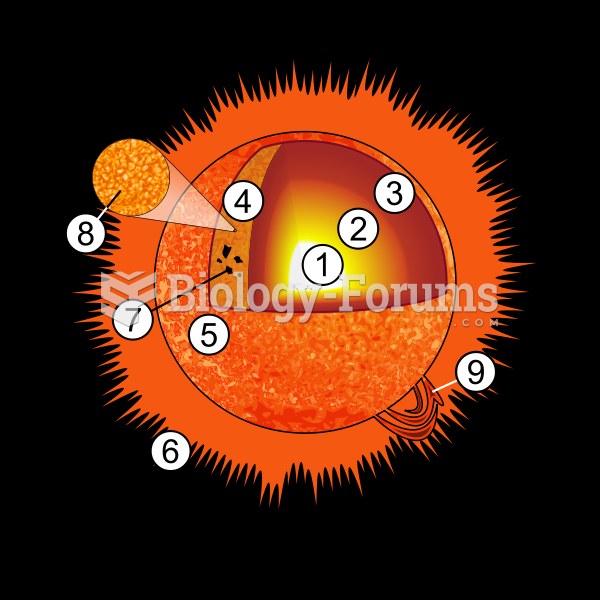
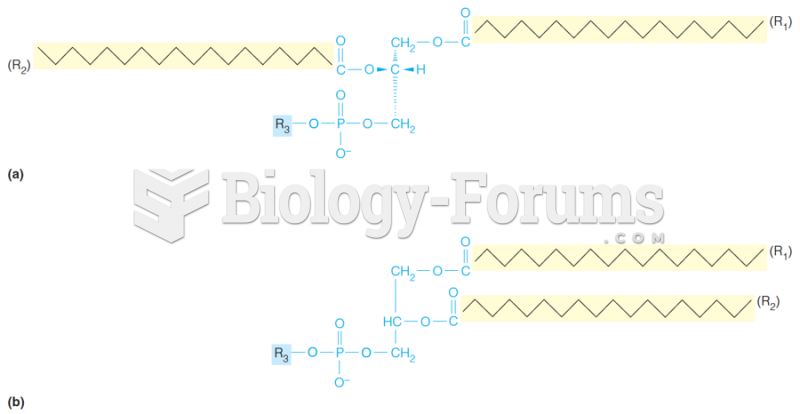
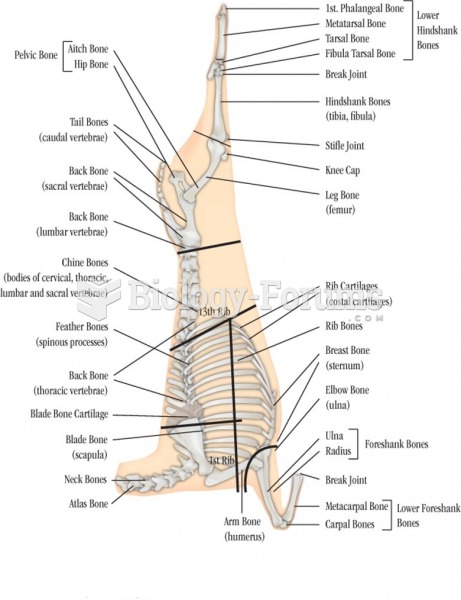
|
|
|
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
About 3% of all pregnant women will give birth to twins, which is an increase in rate of nearly 60% since the early 1980s.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
In 1886, William Bates reported on the discovery of a substance produced by the adrenal gland that turned out to be epinephrine (adrenaline). In 1904, this drug was first artificially synthesized by Friedrich Stolz.