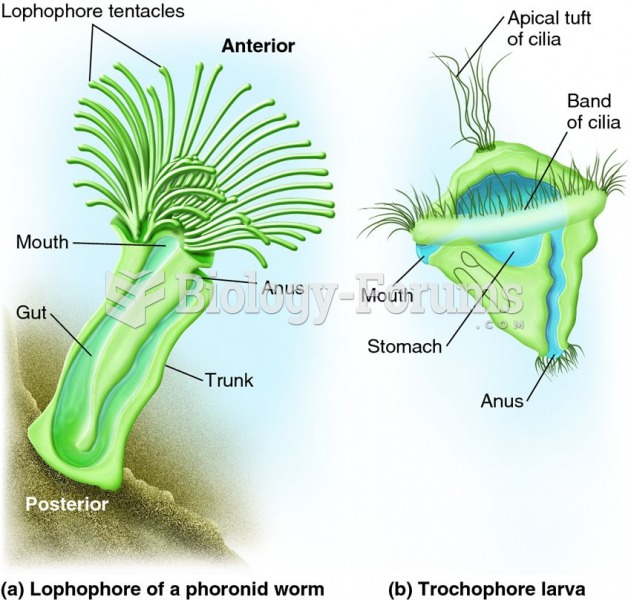
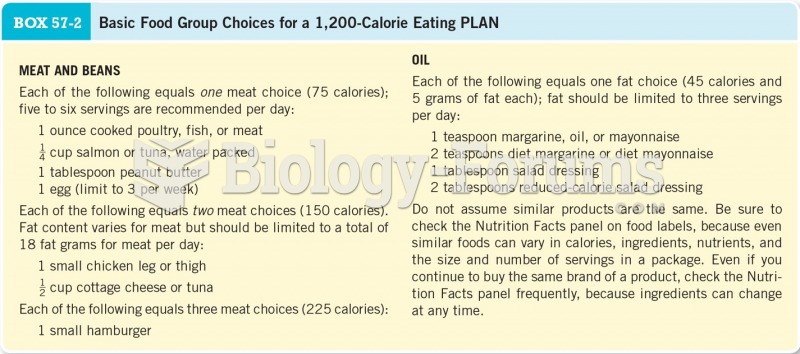
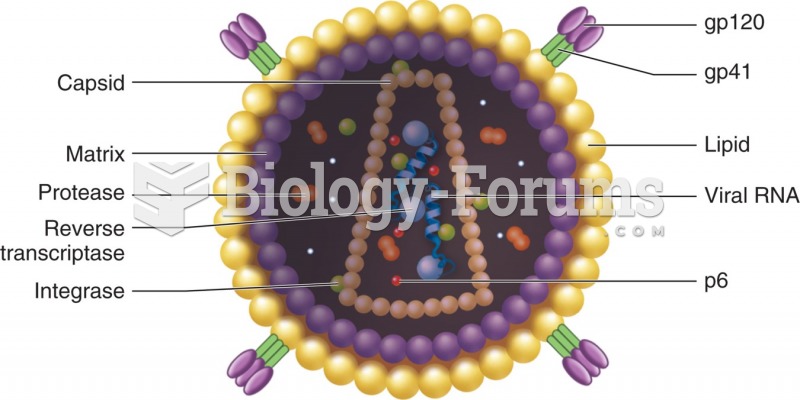
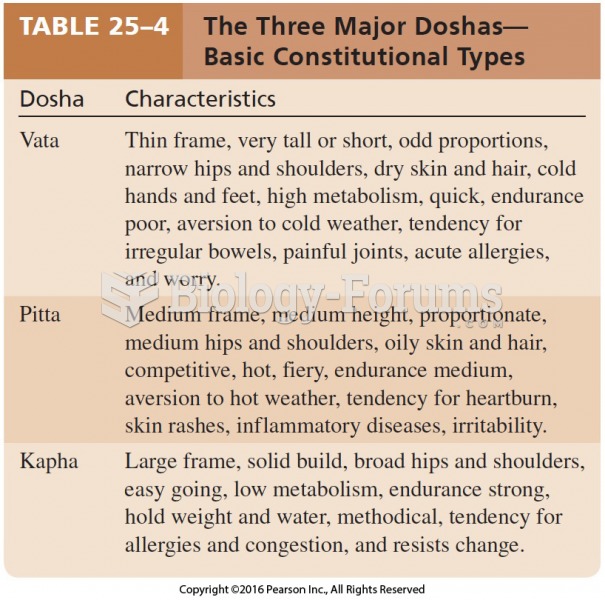
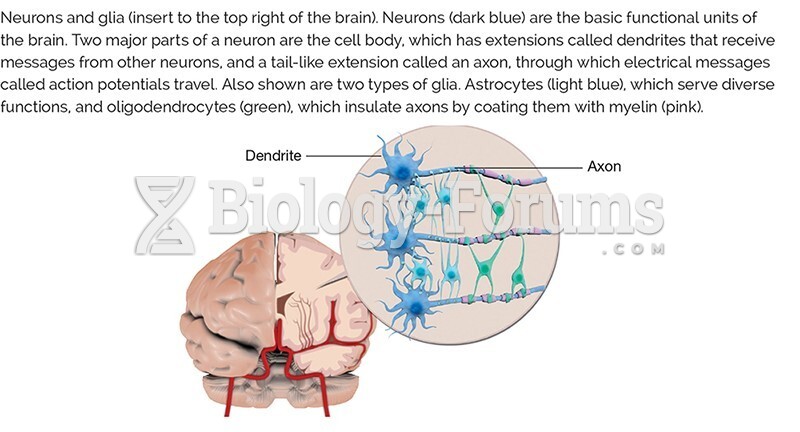
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
Did you know?
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
Did you know?
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
Did you know?
Warfarin was developed as a consequence of the study of a strange bleeding disorder that suddenly occurred in cattle on the northern prairies of the United States in the early 1900s.
Did you know?
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.