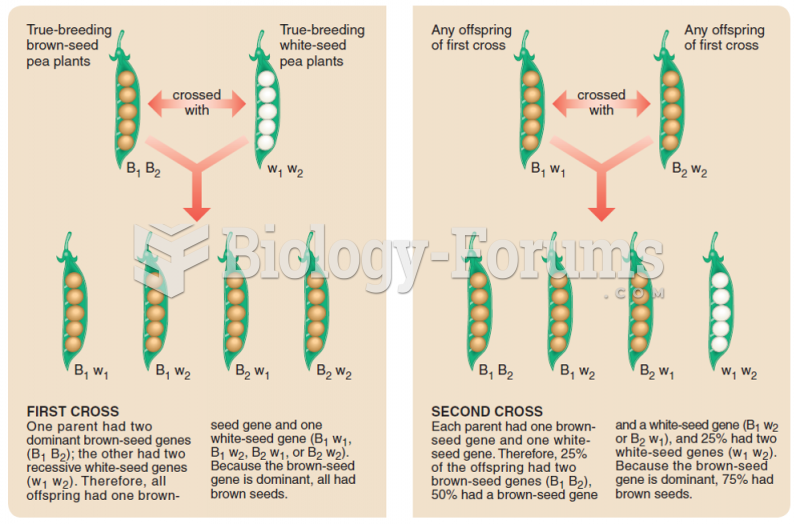
|
|
|
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
The people with the highest levels of LDL are Mexican American males and non-Hispanic black females.
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).