|
|
|
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Before a vaccine is licensed in the USA, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews it for safety and effectiveness. The CDC then reviews all studies again, as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Every lot of vaccine is tested before administration to the public, and the FDA regularly inspects vaccine manufacturers' facilities.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
Patients who cannot swallow may receive nutrition via a parenteral route—usually, a catheter is inserted through the chest into a large vein going into the heart.
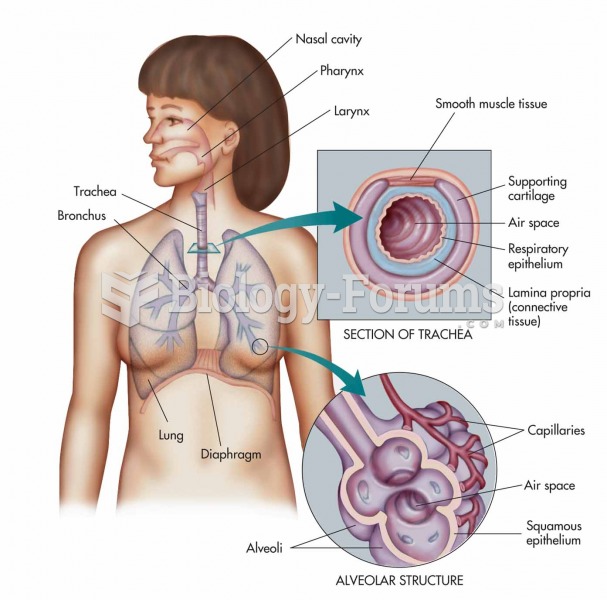 The respiratory system: nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, and lung with expanded vie
The respiratory system: nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, and lung with expanded vie
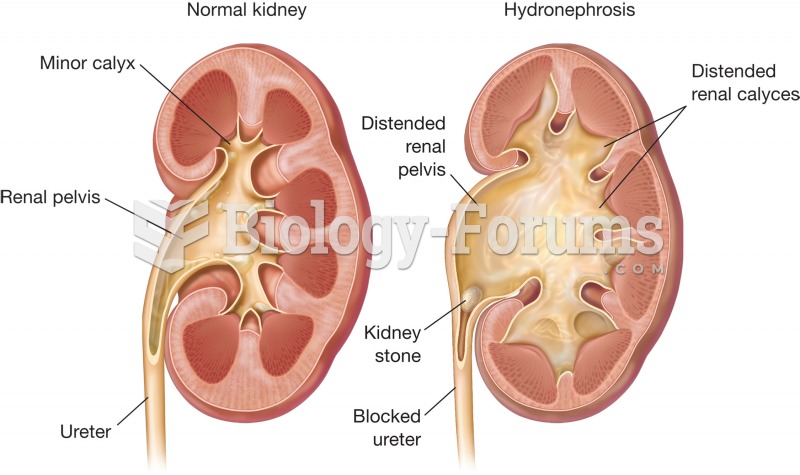
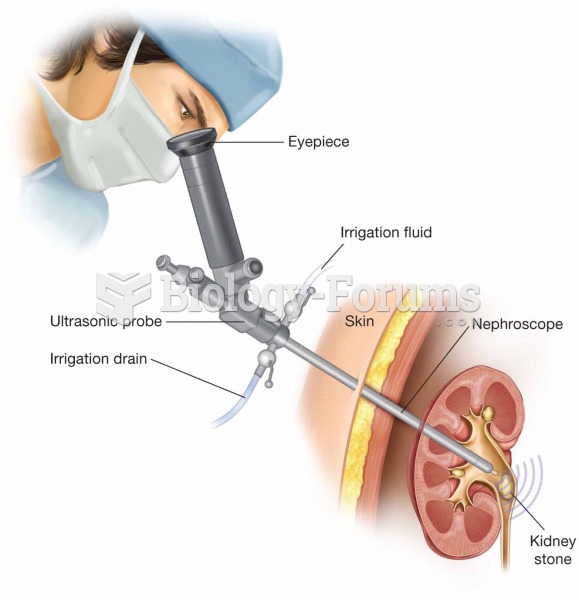 Percutaneous ultrasonic lithotripsy. A nephroscope is inserted into the renal pelvis, and ultrasound
Percutaneous ultrasonic lithotripsy. A nephroscope is inserted into the renal pelvis, and ultrasound