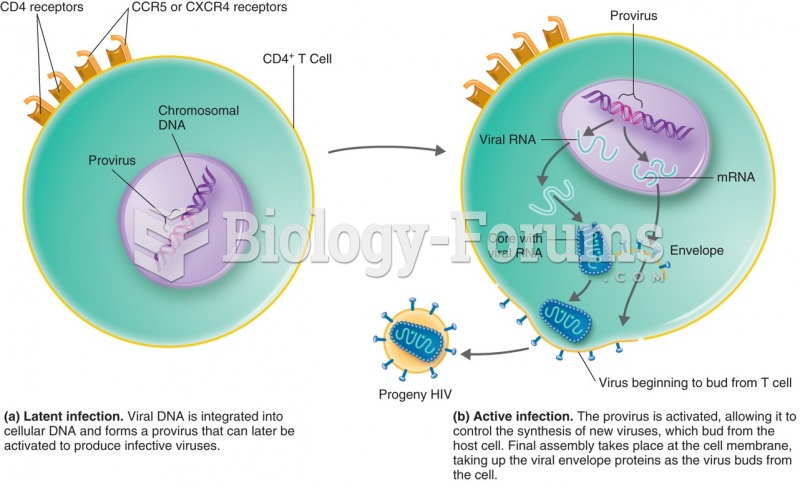
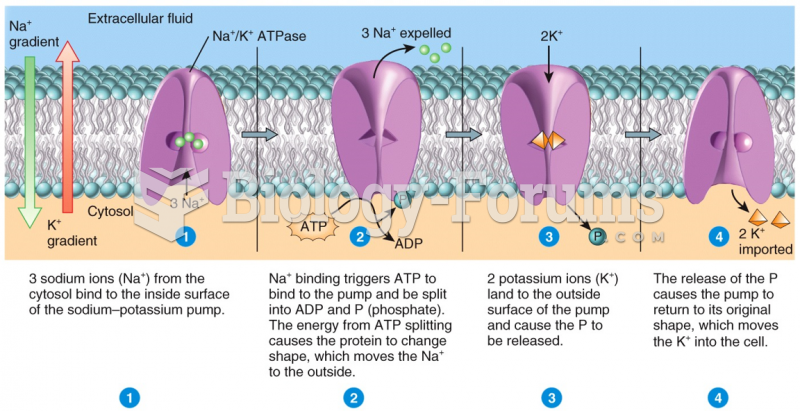
|
|
|
The eye muscles are the most active muscles in the whole body. The external muscles that move the eyes are the strongest muscles in the human body for the job they have to do. They are 100 times more powerful than they need to be.
Hippocrates noted that blood separates into four differently colored liquids when removed from the body and examined: a pure red liquid mixed with white liquid material with a yellow-colored froth at the top and a black substance that settles underneath; he named these the four humors (for blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile).
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
The newest statin drug, rosuvastatin, has been called a superstatin because it appears to reduce LDL cholesterol to a greater degree than the other approved statin drugs.