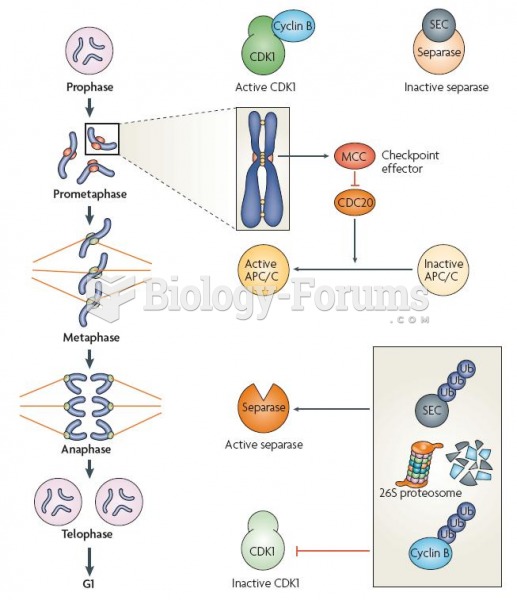
|
|
|
A recent study has found that following a diet rich in berries may slow down the aging process of the brain. This diet apparently helps to keep dopamine levels much higher than are seen in normal individuals who do not eat berries as a regular part of their diet as they enter their later years.
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
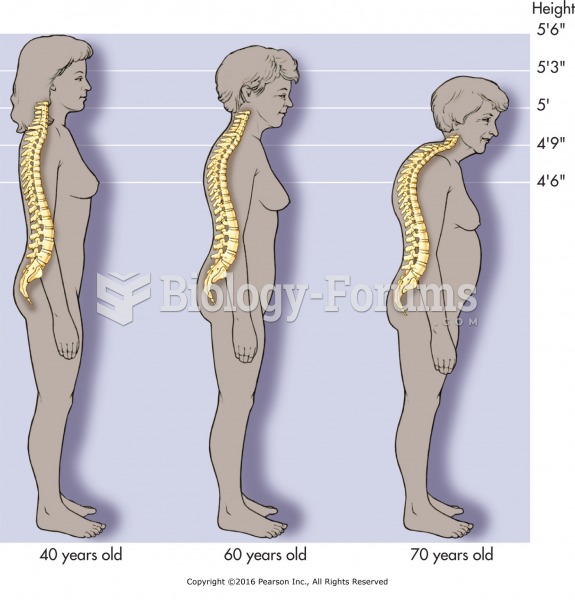
Adolescents often feel clumsy during puberty because during this time of development, their hands and feet grow faster than their arms and legs do. The body is therefore out of proportion. One out of five adolescents actually experiences growing pains during this period.
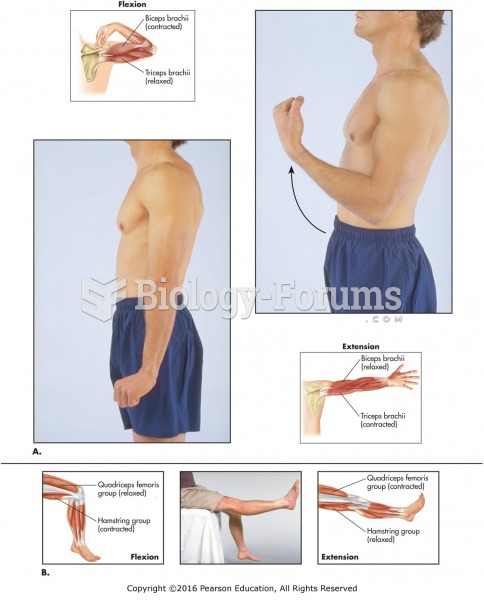 The types of skeletal movement. (A) Flexion and extension of left forearm. (B) Flexion and extension ...
The types of skeletal movement. (A) Flexion and extension of left forearm. (B) Flexion and extension ...
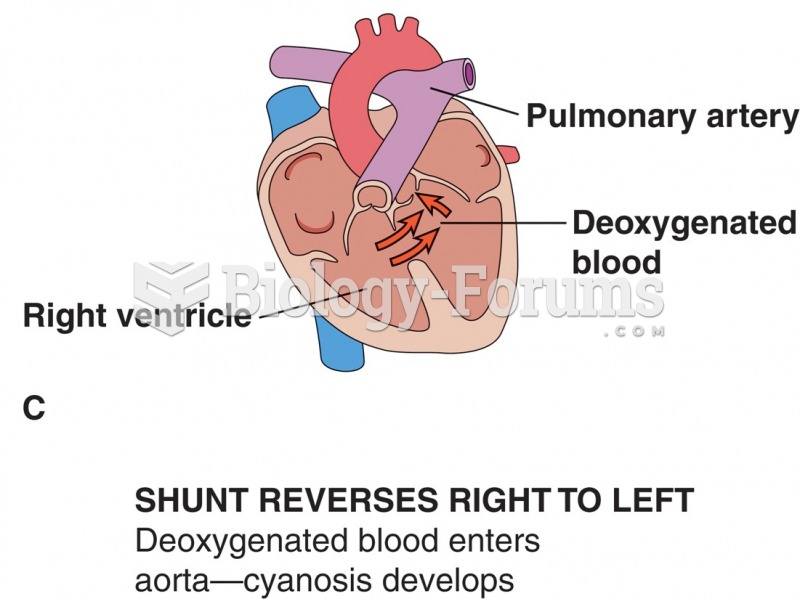 Effects of septal defects: (A) normal shunt; no cyanosis; (B) increased pressure in right ventricle; ...
Effects of septal defects: (A) normal shunt; no cyanosis; (B) increased pressure in right ventricle; ...