|
|
|
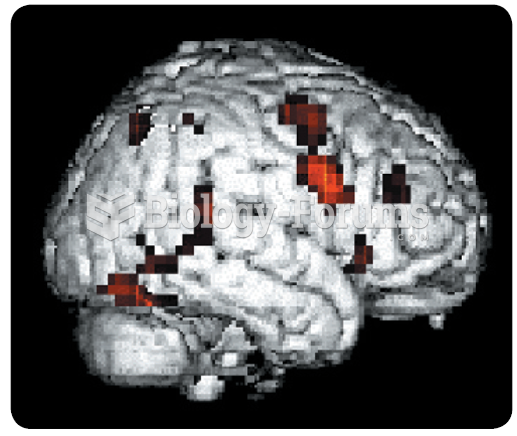
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
Pink eye is a term that refers to conjunctivitis, which is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane (conjunctiva) over the white part of the eye (sclera). It may be triggered by a virus, bacteria, or foreign body in the eye. Antibiotic eye drops alleviate bacterial conjunctivitis, and antihistamine allergy pills or eye drops help control allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
The calories found in one piece of cherry cheesecake could light a 60-watt light bulb for 1.5 hours.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.
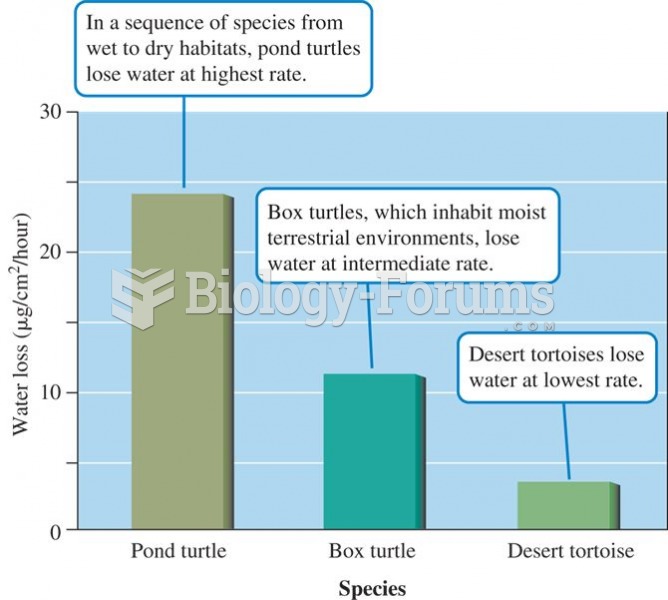 Rates of water loss by two turtles and a tortoise indicate an inverse relationship between the dryne
Rates of water loss by two turtles and a tortoise indicate an inverse relationship between the dryne
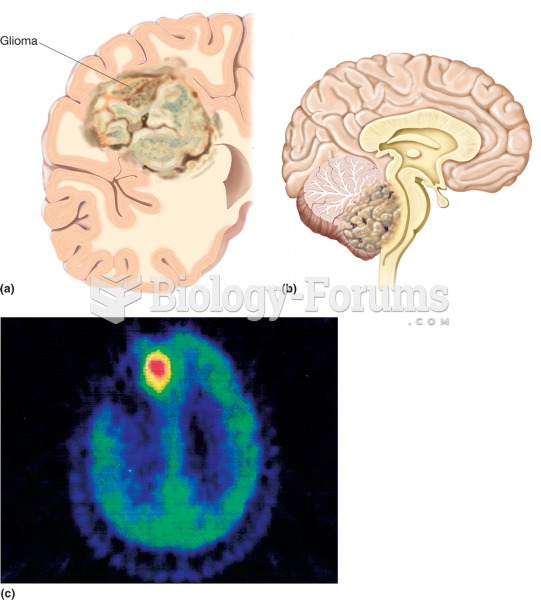 Glioma. (a) Illustration of a large glioma (colored area) within the left cerebral hemisphere in a s
Glioma. (a) Illustration of a large glioma (colored area) within the left cerebral hemisphere in a s