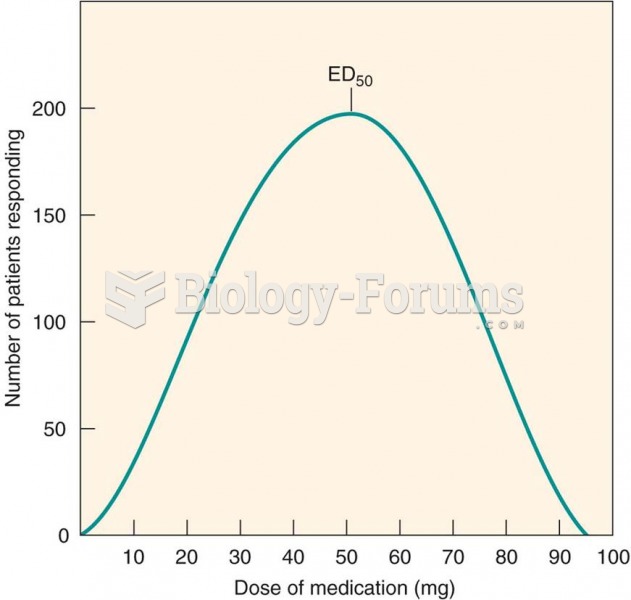
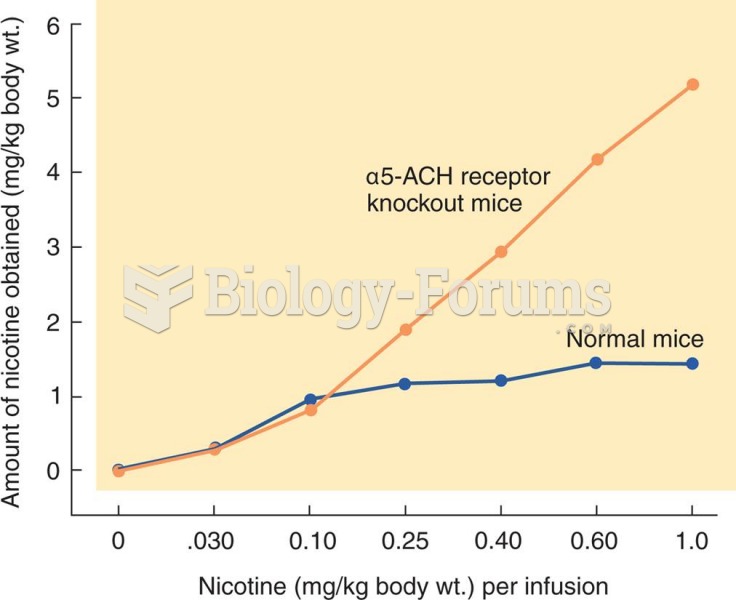
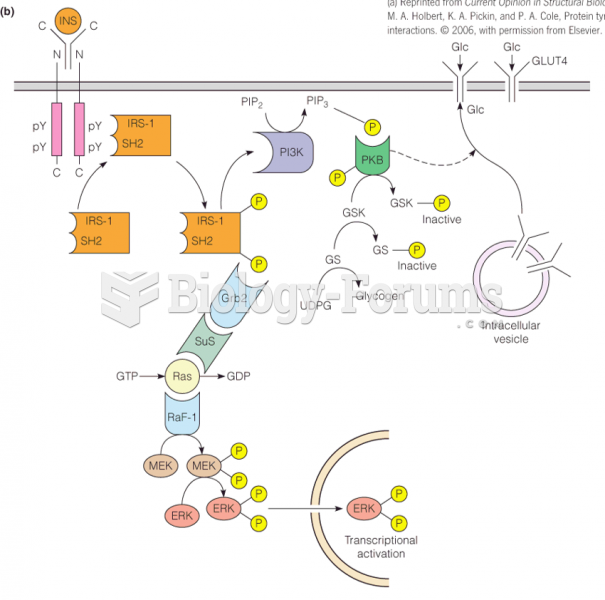
|
|
|
Egg cells are about the size of a grain of sand. They are formed inside of a female's ovaries before she is even born.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates's recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.