|
|
|
The toxic levels for lithium carbonate are close to the therapeutic levels. Signs of toxicity include fine hand tremor, polyuria, mild thirst, nausea, general discomfort, diarrhea, vomiting, drowsiness, muscular weakness, lack of coordination, ataxia, giddiness, tinnitus, and blurred vision.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women age 65 years of age or older should be screened with bone densitometry.
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
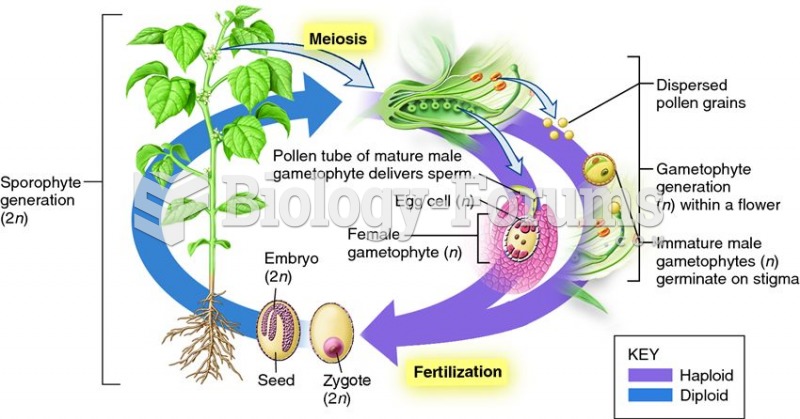 The sexual cycle of flowering plants involves alternation of sporophyte and gametophyte generations.
The sexual cycle of flowering plants involves alternation of sporophyte and gametophyte generations.
 Walter Thompson saw his assets evaporate during the stock market collapse in 1929. Desperate for ...
Walter Thompson saw his assets evaporate during the stock market collapse in 1929. Desperate for ...