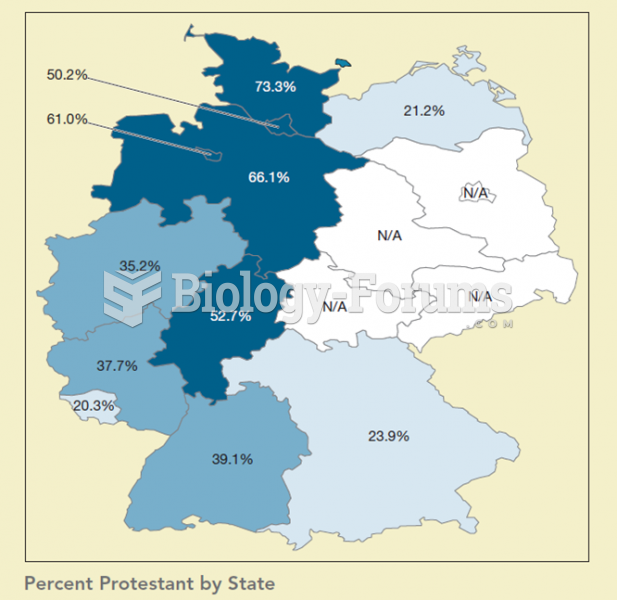
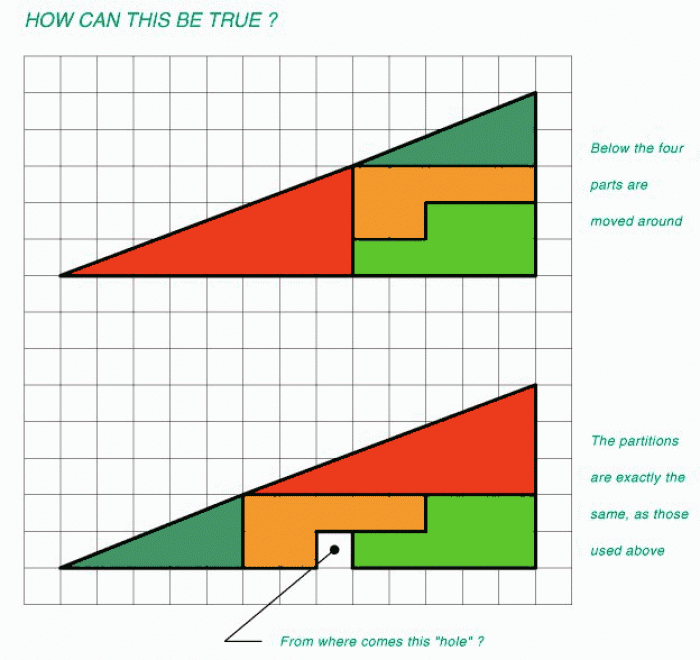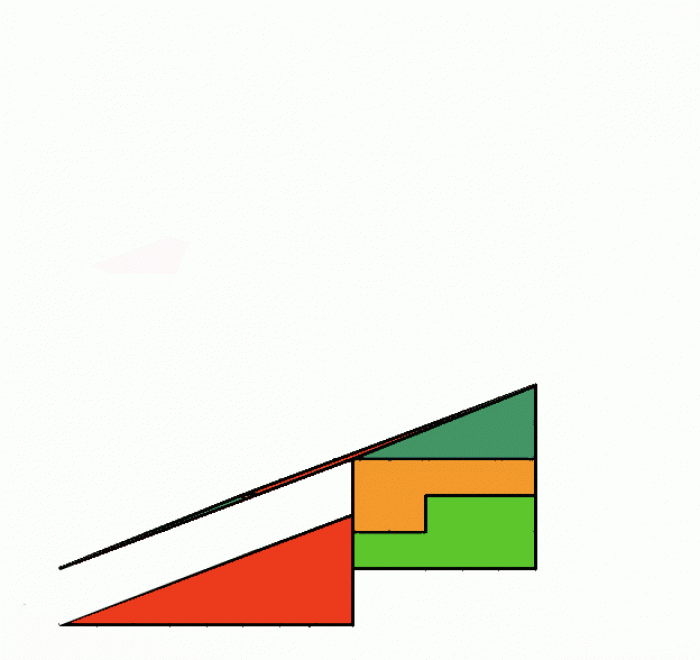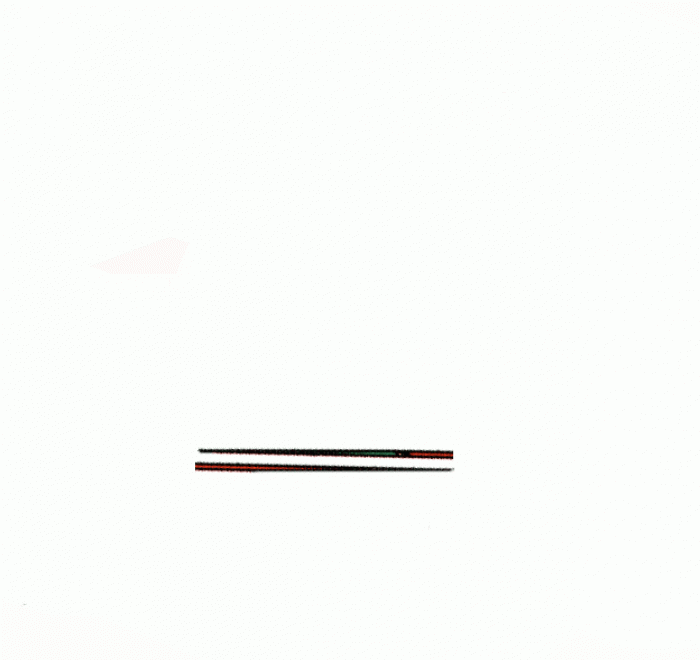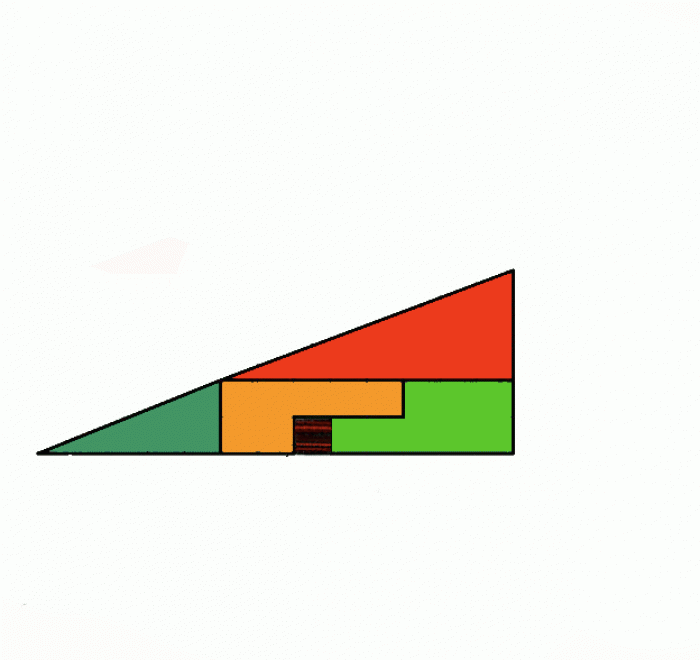
|
|
|
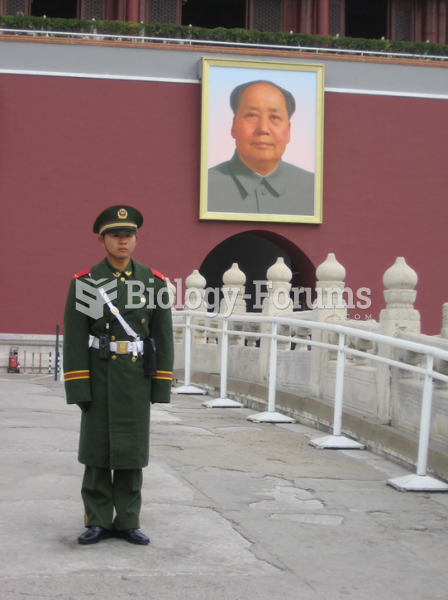
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
Nitroglycerin is used to alleviate various heart-related conditions, and it is also the chief component of dynamite (but mixed in a solid clay base to stabilize it).
Pregnant women usually experience a heightened sense of smell beginning late in the first trimester. Some experts call this the body's way of protecting a pregnant woman from foods that are unsafe for the fetus.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Risperdal, an adult antipsychotic drug, for the symptomatic treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism. The approval is the first for the use of a drug to treat behaviors associated with autism in children. These behaviors are included under the general heading of irritability and include aggression, deliberate self-injury, and temper tantrums.
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.