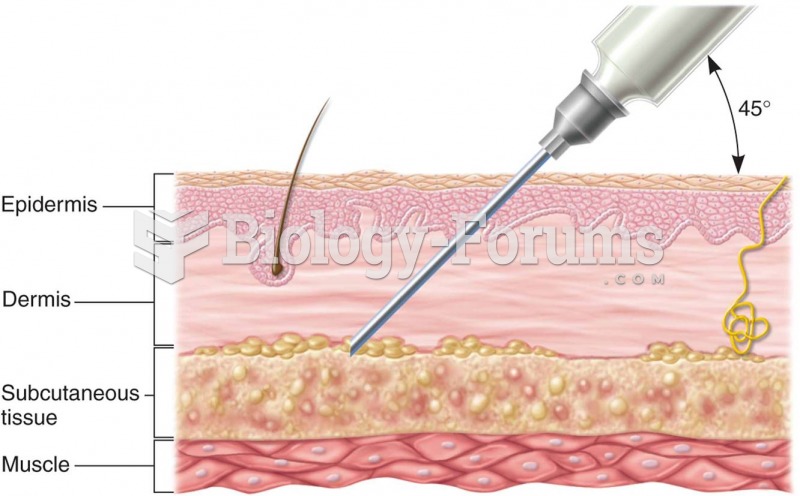
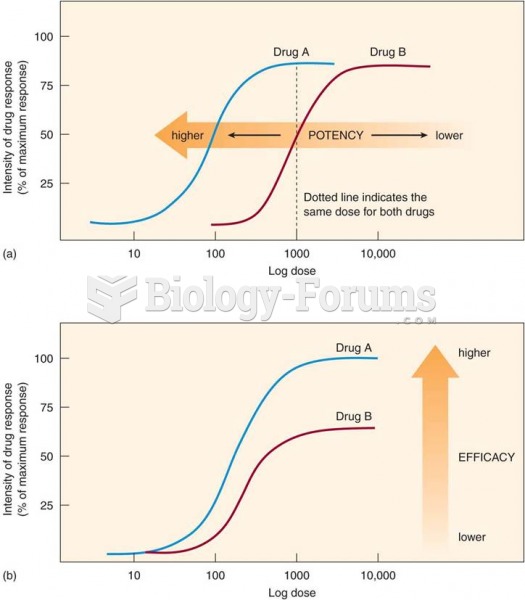
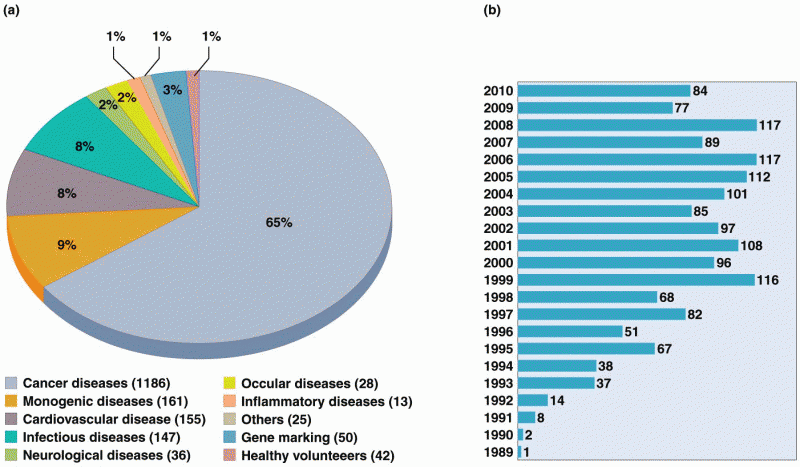
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.
Did you know?
Approximately 25% of all reported medication errors result from some kind of name confusion.
Did you know?
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
Did you know?
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
Did you know?
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.