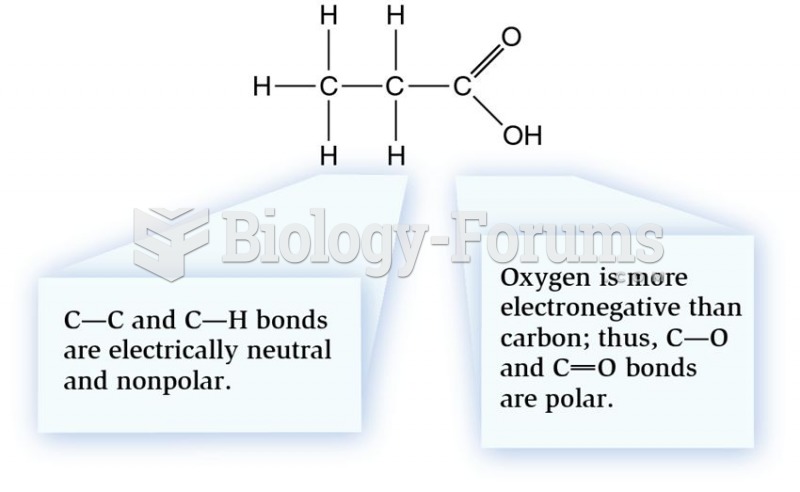
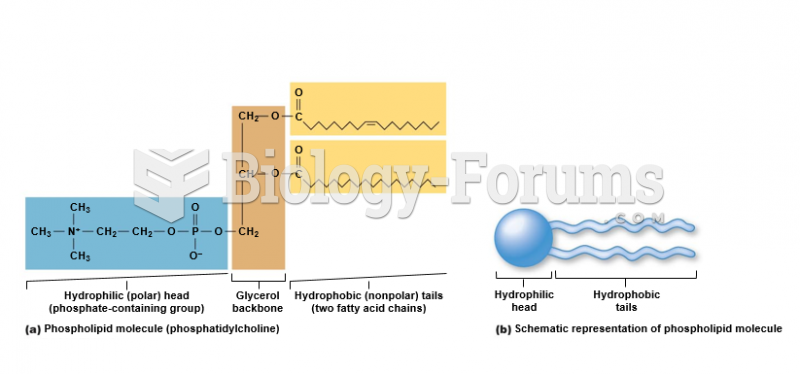
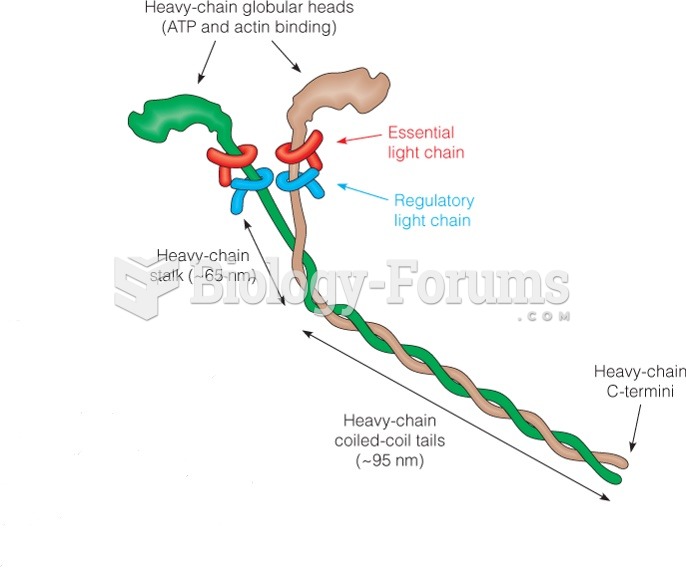
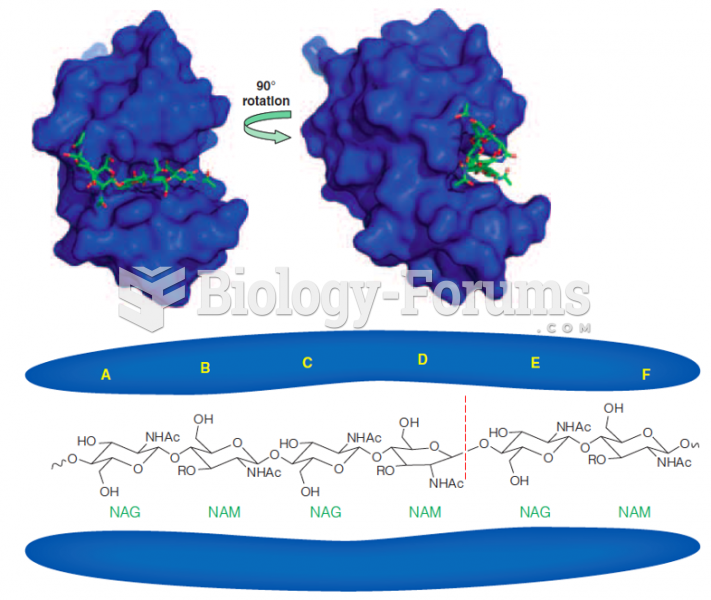
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
Did you know?
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
Did you know?
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
Did you know?
The tallest man ever known was Robert Wadlow, an American, who reached the height of 8 feet 11 inches. He died at age 26 years from an infection caused by the immense weight of his body (491 pounds) and the stress on his leg bones and muscles.
Did you know?
Most fungi that pathogenically affect humans live in soil. If a person is not healthy, has an open wound, or is immunocompromised, a fungal infection can be very aggressive.