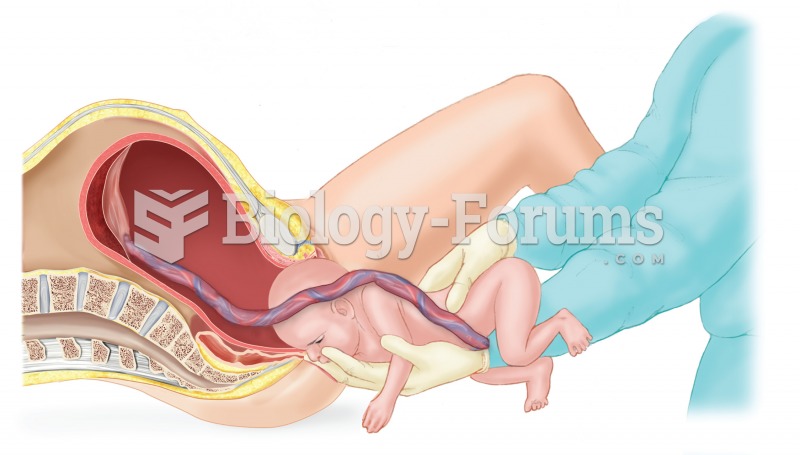
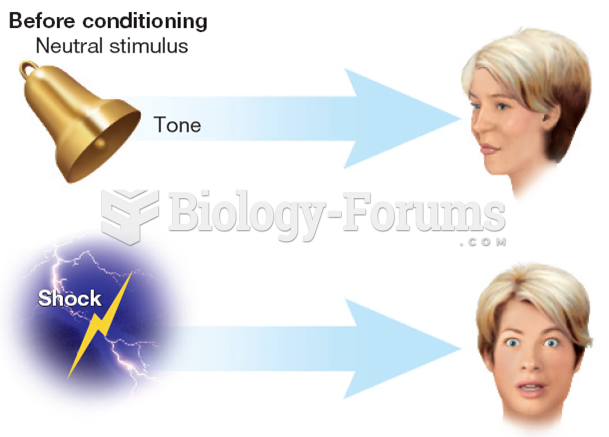
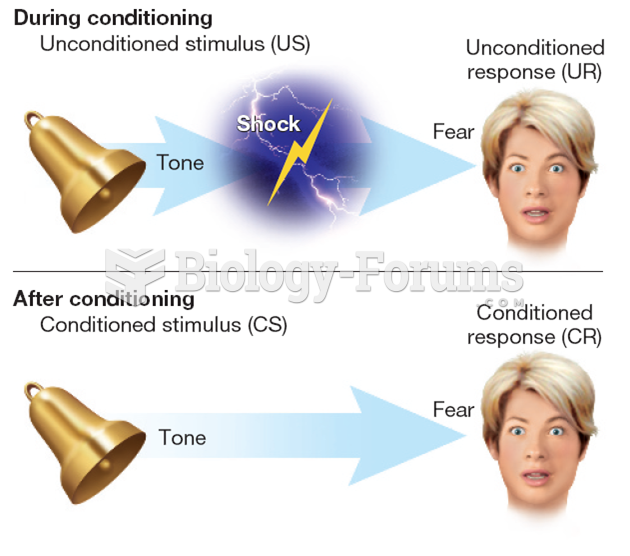
|
|
|
Recent studies have shown that the number of medication errors increases in relation to the number of orders that are verified per pharmacist, per work shift.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
To maintain good kidney function, you should drink at least 3 quarts of water daily. Water dilutes urine and helps prevent concentrations of salts and minerals that can lead to kidney stone formation. Chronic dehydration is a major contributor to the development of kidney stones.
Every 10 seconds, a person in the United States goes to the emergency room complaining of head pain. About 1.2 million visits are for acute migraine attacks.