Answer to Question 1
Toward the end of the 19th century, the German psychiatrist Emil Kraepelin gave us what stands today as the most enduring description and categorization of schizophrenia. Two of Kraepelin's accomplishments are especially important. First, he combined several symptoms of insanity that had usually been viewed as reflecting separate and distinct disorders:
catatonia
(alternating immobility and excited agitation),
hebephrenia
(silly and immature emotionality), and
paranoia
(delusions of grandeur or persecution). Kraepelin thought these symptoms shared similar underlying features and included them under the Latin term
dementia praecox
. Although the clinical manifestation might differ from person to person, Kraepelin believed an early onset at the heart of each disorder develops into mental weakness.. In a second important contribution, Kraepelin distinguished dementia praecox from manic-depressive illness (now called bipolar disorder). For people with dementia praecox, an early age of onset and a poor outcome were characteristic. Kraepelin also noted the numerous symptoms in people with dementia praecox, including hallucinations, delusions, negativism, and stereotyped behavior.
A second major figure in the history of schizophrenia was Kraepelin's contemporary, Eugen Bleuler, a Swiss psychiatrist who introduced the term schizophrenia. The label was significant because it signaled Bleuler's departure from Kraepelin on what he thought was the core problem. Schizophrenia, which comes from the combination of the Greek words for split (skhizein) and mind (phren), reflected Bleuler's belief that underlying all the unusual behaviors shown by people with this disorder was an associative splitting of the basic functions of personality. This concept emphasized the breaking of associative threads, or the destruction of the forces that connect one function to the next. Furthermore, Bleuler believed that a difficulty keeping a consistent train of thought characteristic of all people with this disorder led to the many and diverse symptoms they displayed. Whereas Kraepelin focused on early onset and poor outcomes, Bleuler highlighted what he believed to be the universal underlying problem. Unfortunately, the concept of split mind inspired the common but incorrect use of the term schizophrenia to mean split or multiple personality.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: ABNO.DURA.16.APA4.2 .b - Accurately self-assess performance quality by adhering to external standards
Answer to Question 2
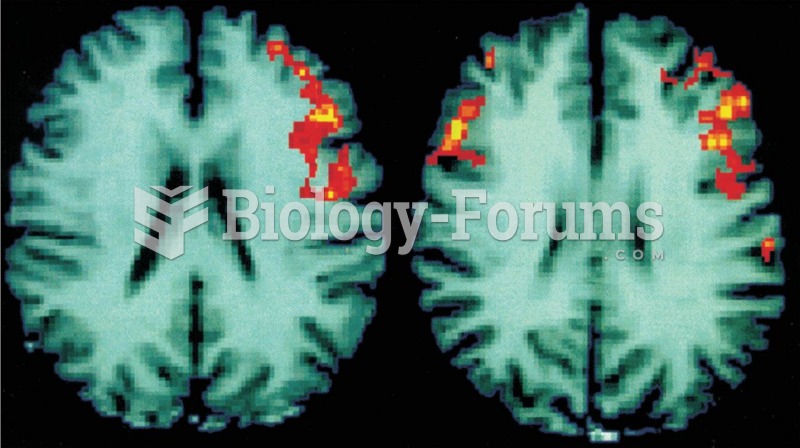
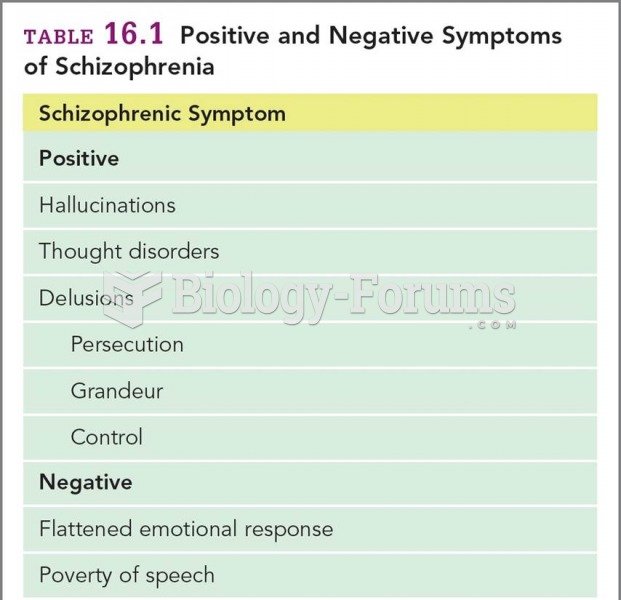
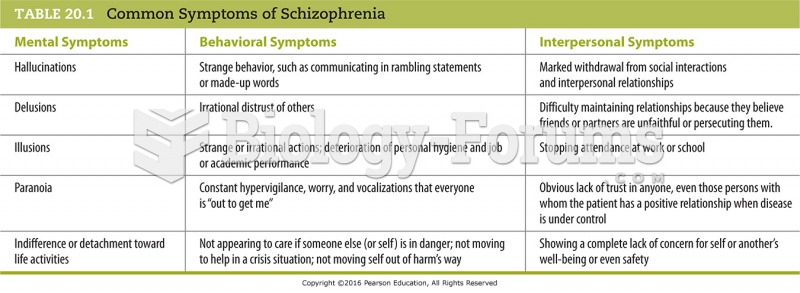
The positive symptoms of schizophrenia involve the active manifestations of abnormal behavior including delusions and hallucinations, inappropriate affect, and formal thought disorders. Negative symptoms usually indicate the absence or insufficiency of normal behavior in areas such as poverty of speech, lack of motivation, and flat or blunted affect. A diagnosis of schizophrenia requires that two or more positive, negative, and/or disorganized symptoms be present for at least one month.
People with schizophrenia have a poorer prognosis than those with most of the other disordersincluding a high risk of suicidealthough a significant number of individuals can experience long periods of recovery. Treatment typically involves antipsychotic drugs that are usually administered with a variety of psychosocial treatments, with the goal of reducing relapse and improving skills in deficits and compliance in taking the medications. The effectiveness of treatment is limited, because schizophrenia is typically a chronic disorder.