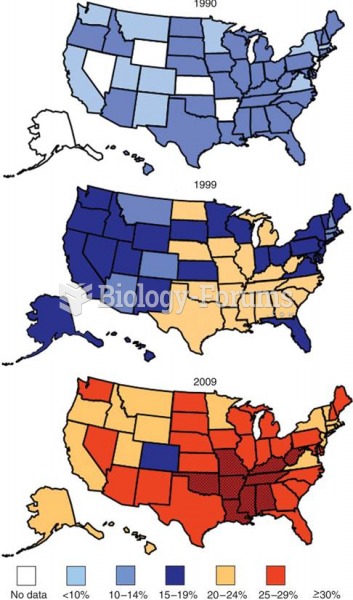
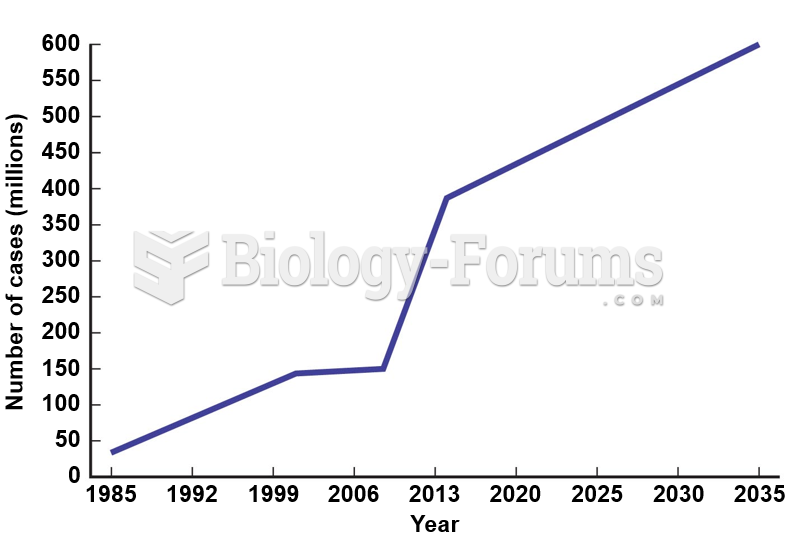
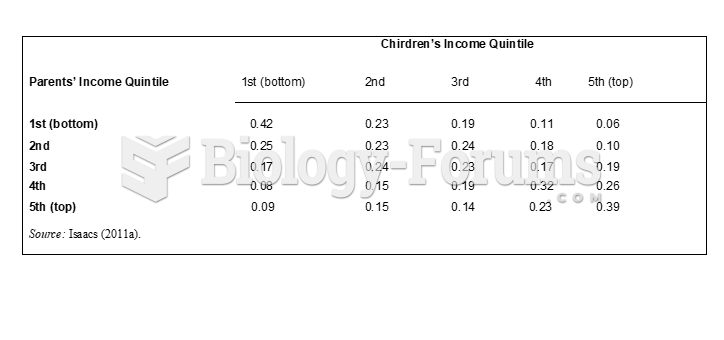
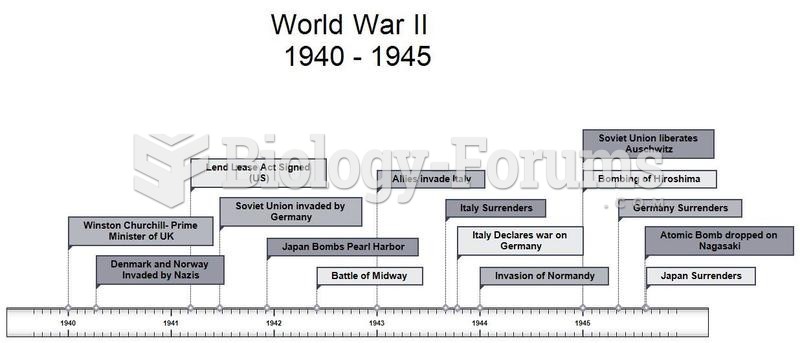
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Eat fiber! A diet high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by as much as 10%.
Did you know?
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
Did you know?
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.
Did you know?
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.
Did you know?
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.