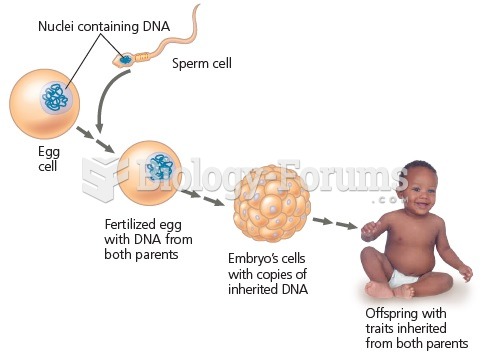
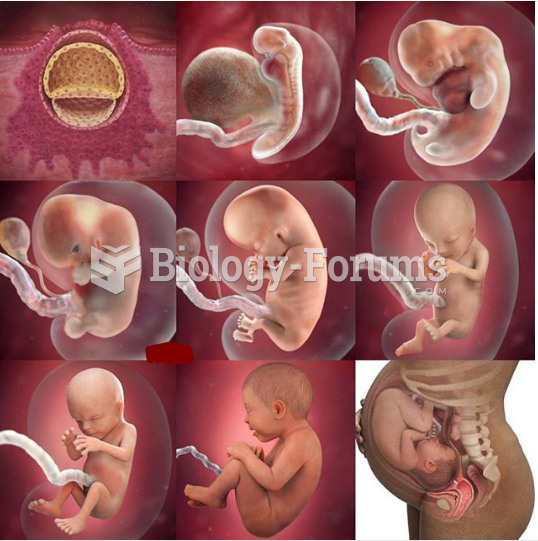
|
|
|
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Cocaine was isolated in 1860 and first used as a local anesthetic in 1884. Its first clinical use was by Sigmund Freud to wean a patient from morphine addiction. The fictional character Sherlock Holmes was supposed to be addicted to cocaine by injection.
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.
About 100 new prescription or over-the-counter drugs come into the U.S. market every year.
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.