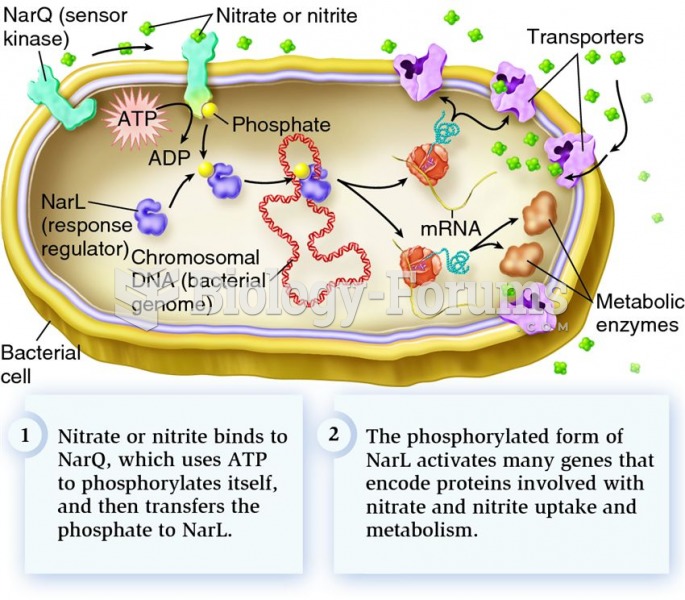
|
|
|
Oxytocin is recommended only for pregnancies that have a medical reason for inducing labor (such as eclampsia) and is not recommended for elective procedures or for making the birthing process more convenient.
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.