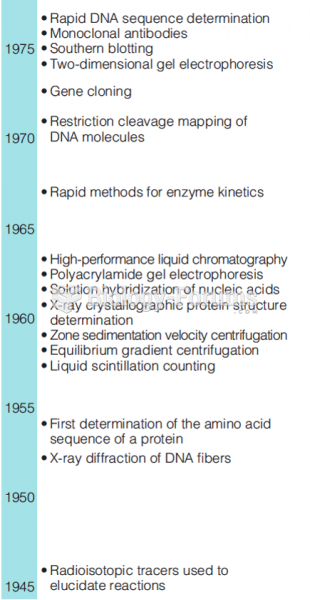
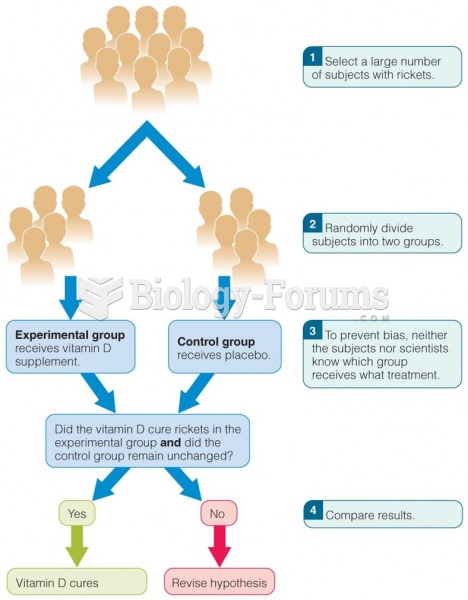
Answer to Question 1
Anorexia has been observed in Western countries as well as every non-Western region of the world, suggesting that anorexia may not be a culture-bound syndrome as once believed (Sohl, Touyzl, & Surgenor, 2006). It is becoming increasingly clear that eating disorders do not always manifest the same way in different cultures. In Hong Kong, for example, studies suggest that anorexia may be divided into fat-phobic and nonfat-phobic subtypes and that questionnaires used in Western countries to assess eating disorders may not be sufficiently sensitive to detect the Chinese nonfat-phobic subtype (Lee, Lee, & Leung, 1998). However, the cross-cultural evidence for bulimia and BED outside of a Western context tells a different story. Keel and Klump's (2003) review of culture and eating disorders found no studies reporting the presence of bulimia in individuals who have not been exposed to Western ideals. Epidemiological data for bulimia in non-Western nations suggest that bulimia has a lower prevalence than anorexia in these countries, and even when it is found in non-Western nations, it is not found in the absence of Western influence. A meta-analysis examining the role of ethnicity and culture in the development of eating disturbances found few differences across ethnic groups for bulimia (Wildes & Emery, 2001). These findings seem to suggest that bulimia is a culture-bound syndrome, arising predominantly in Western regions of the world or in places where individuals probably or definitely have been exposed to Western ideals and culture (Anderson-Fye, 2009).
Answer to Question 2
There is increased recognition that eating disorders are more common among young men than was originally believed. Males also are subjected to powerful media images, although perhaps not to the same extent as females. The increasingly muscular male body ideal may be contributing to body dissatisfaction, disordered eating, and harmful weight-control or body-building behaviors (Smolak & Stein, 2010). Young men with eating disorders show some of the same clinical features as young women with eating disorders. However, young men show less of a preoccupation with food or a drive for thinness; rather, they want to be more muscular than they actually are and more muscular than the average male body (Olivardia et al., 2004). In addition, young men and boys are more likely to engage in excessive exercising and overeating, whereas young women and girls are more likely to engage in purging behaviors, to report loss of control while eating, and to try to reduce their caloric intake (von Ranson & Wallace, 2014).
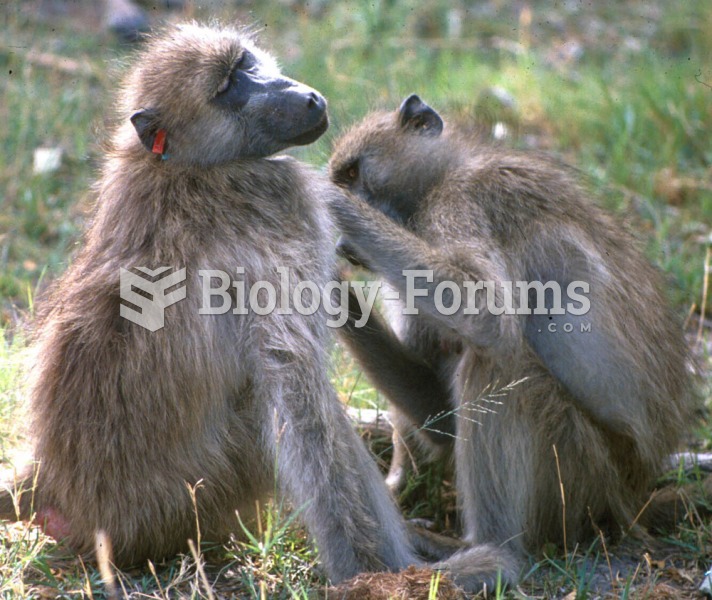 A recent study found that female baboons that groom each other are more likely to come to each other
A recent study found that female baboons that groom each other are more likely to come to each other
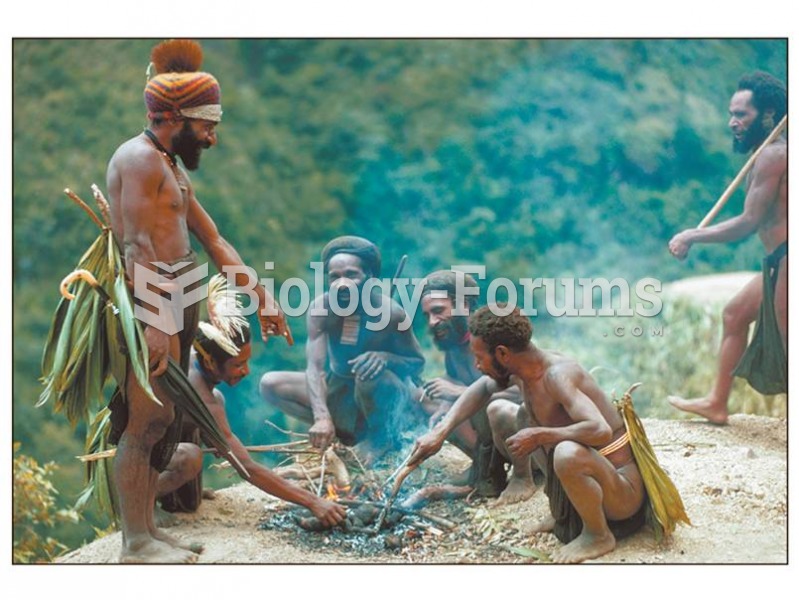 Evolutionary ecologists live and do research in contemporary cultures that maintain all or some aspe
Evolutionary ecologists live and do research in contemporary cultures that maintain all or some aspe