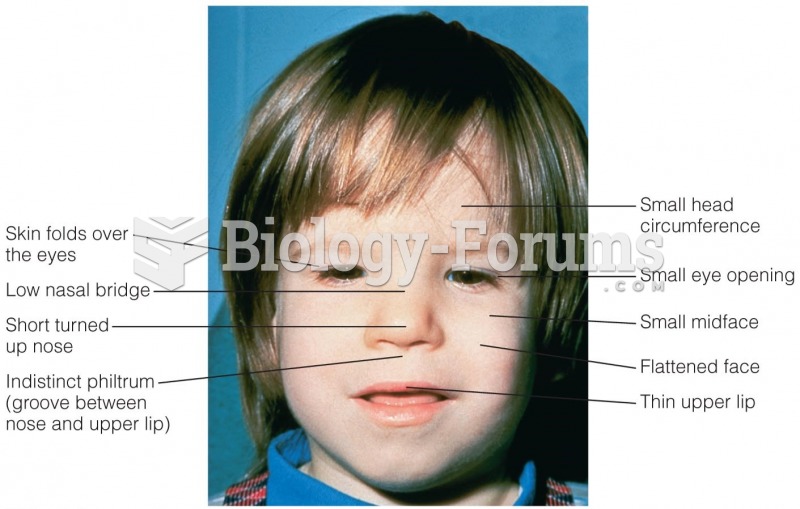
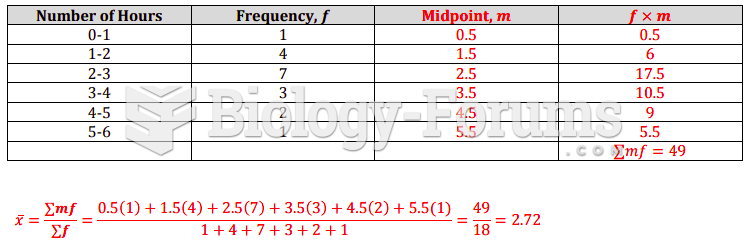
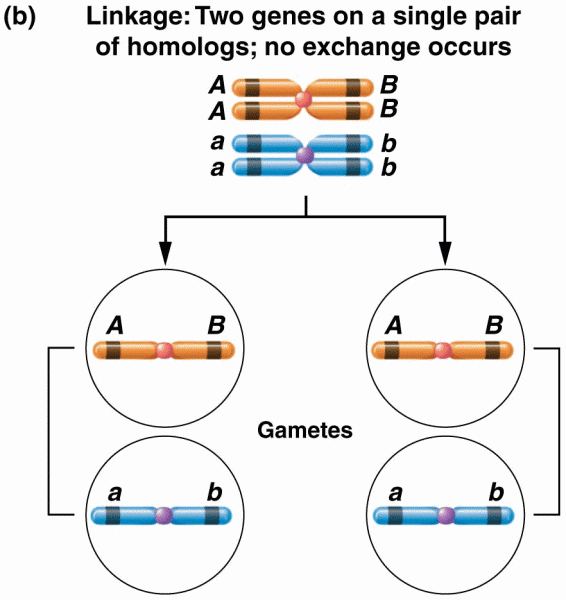
Answer to Question 1
These children worry about being separated from their parents, trying something new, taking tests, making social contacts, or visiting the doctor. They may feel tense or uneasy and constantly seek reassurance that they are safe and protected. Because these anxieties are unrealistic, more frequent, and more intense than normal, they have a negative impact on the child's thinking and behavior.
Answer to Question 2
Children with ADHD who display inattentive and depressive/anxious symptoms tend to report lower self-esteem, whereas those with symptoms of hyperactivityimpuls ivity and conduct problems appear to exaggerate their self-worth (Owens et al., 2007). The bias in the latter group is most dramatic in the areas of performance in which the child is most severely impaired. Increases in positively biased self-perceptions of behavior in children with ADHD have also been found to predict greater aggression over time. Several explanations for the positive bias in children with hyperactivityimpuls ivity have been proposedit serves a self-protective function that allows the child to cope every day despite frequent failures; it reflects a diminished self-awareness as a result of impairments in executive functions (McQuade et al., 2011); or it is a result of not knowing what constitutes successful or unsuccessful performance (Ohan & Johnston, 2002). To date, there is some support for the self-protective function of positive bias (Hoza et al., 2010), although other explanations may also apply.