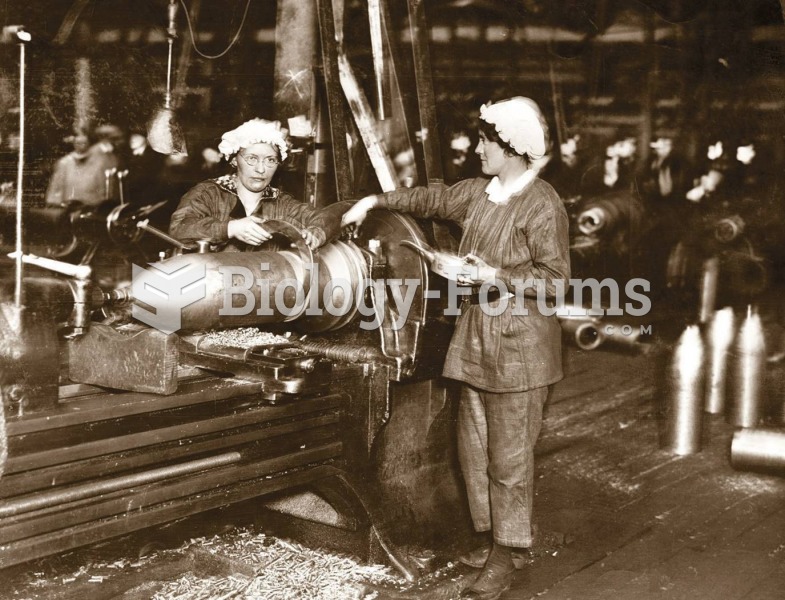
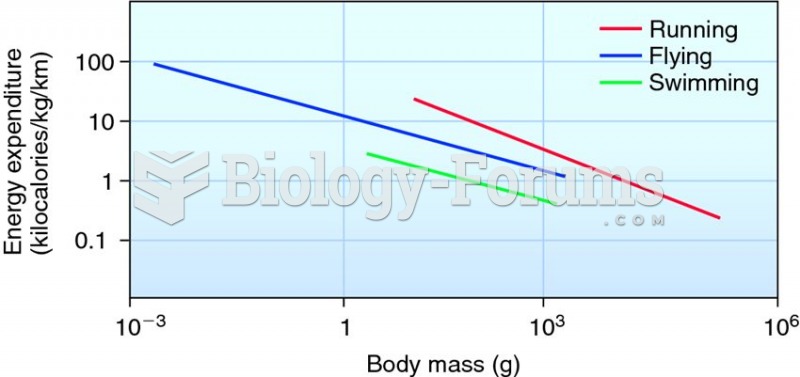
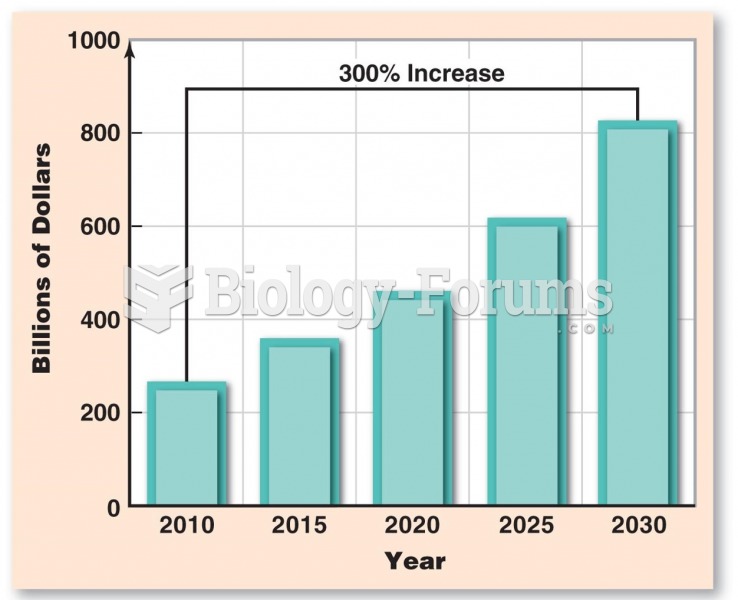
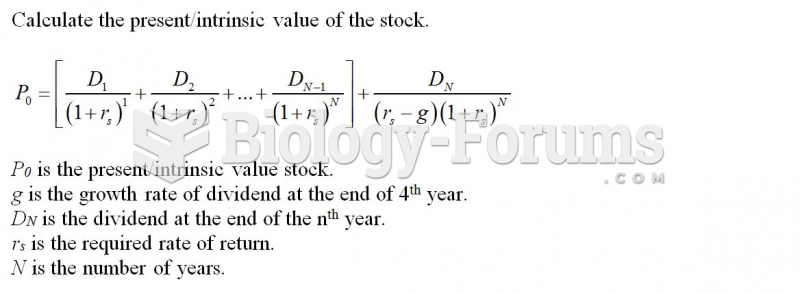
|
|
|
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
More than 20 million Americans cite use of marijuana within the past 30 days, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). More than 8 million admit to using it almost every day.
About 3.2 billion people, nearly half the world population, are at risk for malaria. In 2015, there are about 214 million malaria cases and an estimated 438,000 malaria deaths.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.