Answer to Question 1
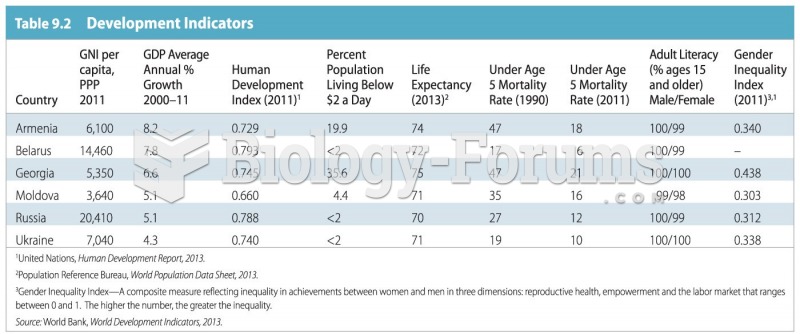
poverty
Answer to Question 2
The three criteria commonly used to evaluate assessment procedures are reliability, validity, and standardization. Reliability refers to the consistency or repeatability of results. There are three different types of reliability: test-retest, internal consistency, and interrater. Test-retest reliability refers to the consistency of a test over time. For example, if you take a test measuring your intelligence one week and the test has good test-retest reliability, your score should be about the same if you take the test again the following week. The second type of reliability is internal consistency. This type of reliability refers to the consistency among test items. In other words, to what extent do the items in a test measure the same construct? The third type of reliability is interrater reliability, which refers to consistency or agreement among scorers or observers. For example, if two researchers were observing children on a playground and counting the frequency with which they engaged in aggressive behavior, then the observers should have similar frequency counts for their assessment to be considered to have good interrater reliability.
Validity addresses the issue of the extent to which a test measures what it is supposed to. There are four main types of validity: predictive validity, content validity, criterion-related validity, and construct validity. Predictive validity refers to the ability for a test to forecast how a person will behave or respond. For example, universities use applicants' ACT and SAT scores to predict future college academic performance. Content validity means that the items of an assessment device are representative examples of the domain(s) the test measures. For example, if a test measures anxiety but its questions asked about a person's social activities, it would not have adequate content validity. A third type of validity is criterion-related validity. With this type of validity, the scores on a measure are compared with a criterion thought to be related to the construct measured by the test. The criterion can be some future event (if so, it is called predictive validity) or some current event (if so, it is called concurrent validity). For example, if I had a test that was supposed to measure how successful one was going to be in college, I might give my test to a group of high school seniors. Then four years later I would compare their scores on the test with their college GPA to see if my test had good predictive validity. For construct validity, test results must be related to the theoretical construct (or concept) the test is supposed to measure. The third criterion is utility, or usefulness. For an assessment to be useful it must be reliable and valid, and provide information that cannot be obtained more simply, cheaply, or quickly using another procedure.
Standardization refers to both the use of identical procedures in administering tests and to establishing norms against which an individual is tested. Results can be compromised if a test administrator treats people differently, such as smiling at one group of children taking a test and being cold and indifferent to another group taking the same test, or giving one group more time than another group (i.e., different procedures in test administration). Also, comparing the scores of a 10-year-old student from Nigeria with those of a college-educated, 50--year-old CEO of a Fortune 500 company would not be valid (different norms based on age, culture, education, experience, etc.).