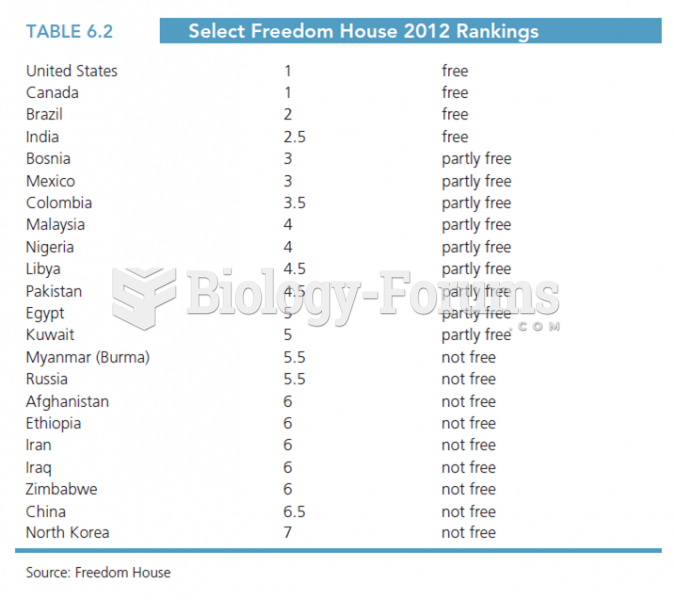
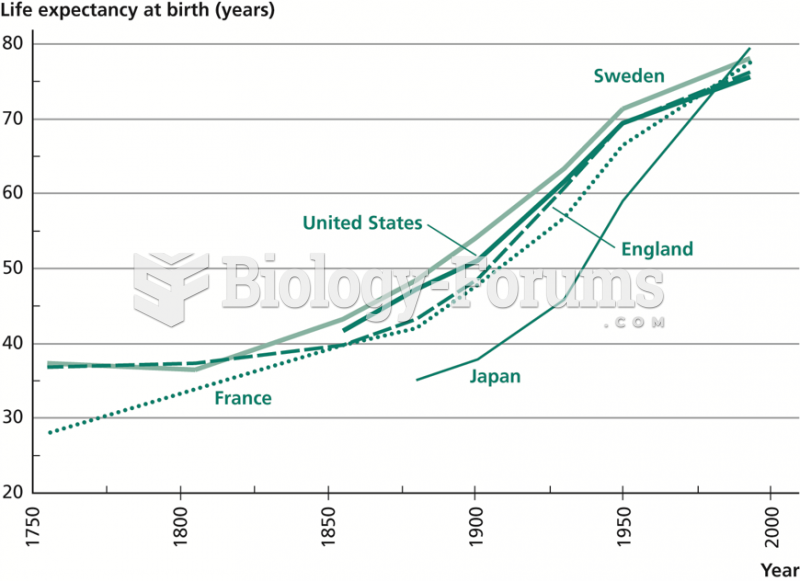
|
|
|
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.
People with alcoholism are at a much greater risk of malnutrition than are other people and usually exhibit low levels of most vitamins (especially folic acid). This is because alcohol often takes the place of 50% of their daily intake of calories, with little nutritional value contained in it.
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
The first successful kidney transplant was performed in 1954 and occurred in Boston. A kidney from an identical twin was transplanted into his dying brother's body and was not rejected because it did not appear foreign to his body.