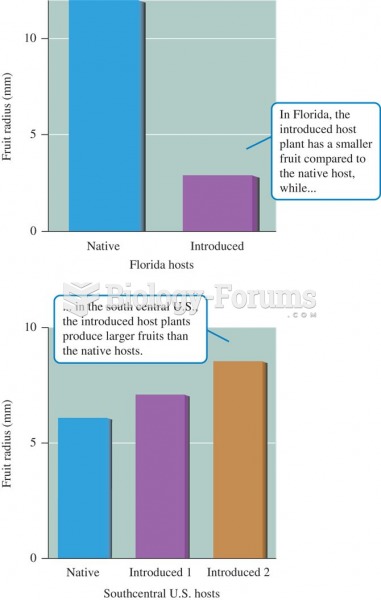
|
|
|
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.