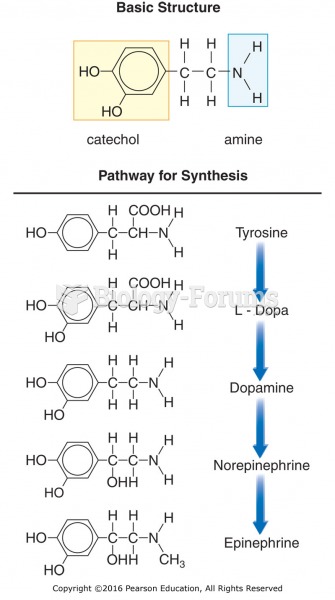
|
|
|
Did you know?
Green tea is able to stop the scent of garlic or onion from causing bad breath.
Did you know?
Bacteria have been found alive in a lake buried one half mile under ice in Antarctica.
Did you know?
There are more sensory neurons in the tongue than in any other part of the body.
Did you know?
Coca-Cola originally used coca leaves and caffeine from the African kola nut. It was advertised as a therapeutic agent and "pickerupper." Eventually, its formulation was changed, and the coca leaves were removed because of the effects of regulation on cocaine-related products.
Did you know?
Opium has influenced much of the world's most popular literature. The following authors were all opium users, of varying degrees: Lewis Carroll, Charles, Dickens, Arthur Conan Doyle, and Oscar Wilde.
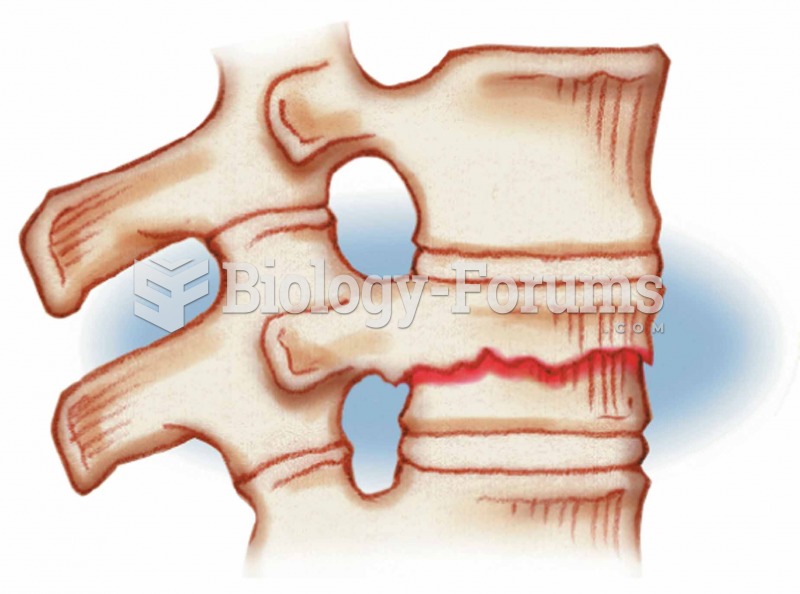 Compression Occurs in vertebrae subjected to extreme stresses, as when one falls and lands on his or
Compression Occurs in vertebrae subjected to extreme stresses, as when one falls and lands on his or
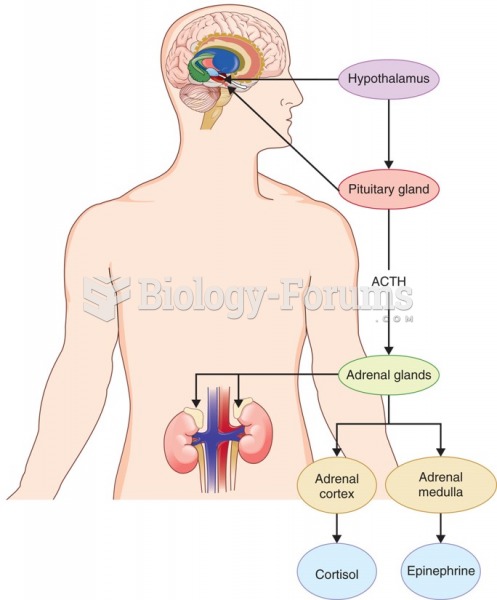 According to neuroendocrine models of depression, repeated or chronic stress results in overactivity ...
According to neuroendocrine models of depression, repeated or chronic stress results in overactivity ...