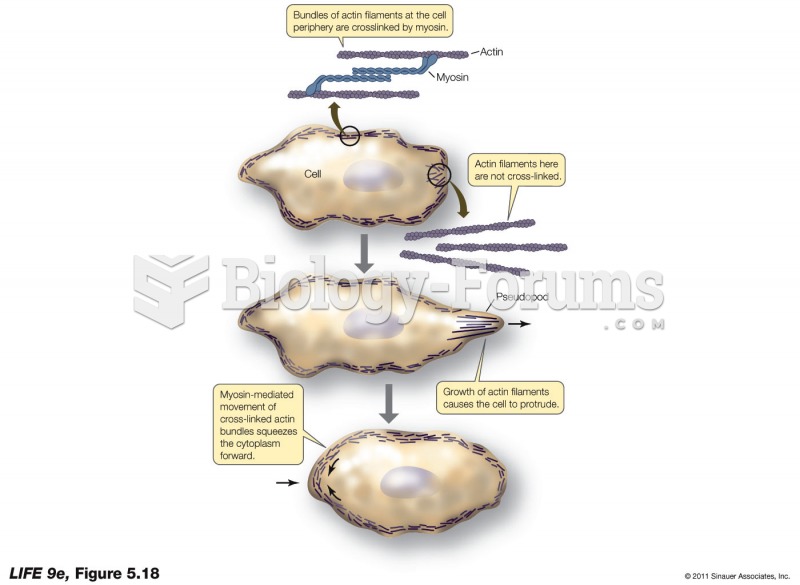
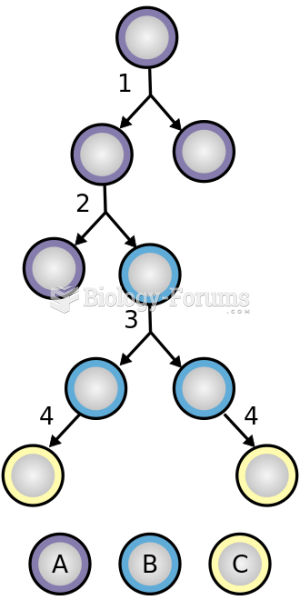
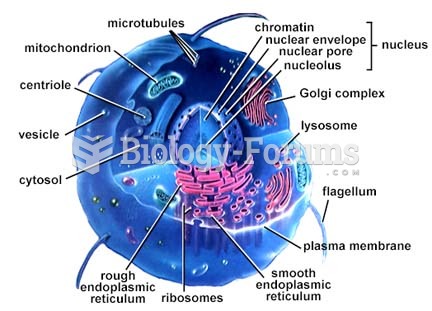
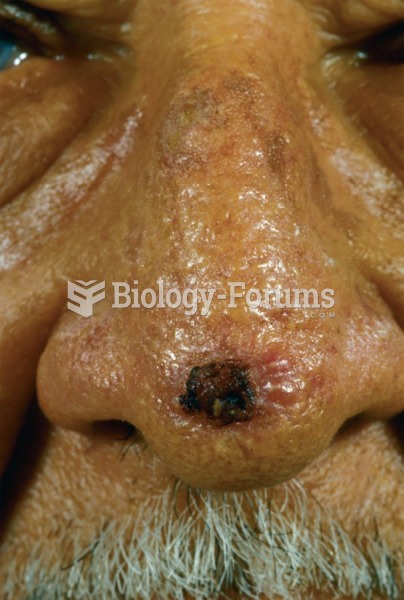
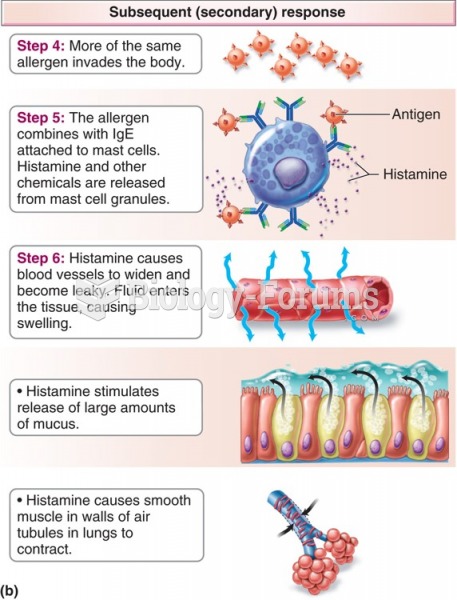
|
|
|
Despite claims by manufacturers, the supplement known as Ginkgo biloba was shown in a study of more than 3,000 participants to be ineffective in reducing development of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in older people.
There used to be a metric calendar, as well as metric clocks. The metric calendar, or "French Republican Calendar" divided the year into 12 months, but each month was divided into three 10-day weeks. Each day had 10 decimal hours. Each hour had 100 decimal minutes. Due to lack of popularity, the metric clocks and calendars were ended in 1795, three years after they had been first marketed.
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.