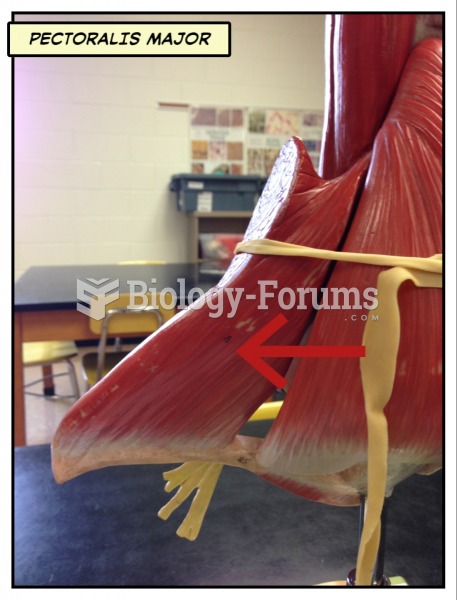
|
|
|
Women are two-thirds more likely than men to develop irritable bowel syndrome. This may be attributable to hormonal changes related to their menstrual cycles.
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
As of mid-2016, 18.2 million people were receiving advanced retroviral therapy (ART) worldwide. This represents between 43–50% of the 34–39.8 million people living with HIV.
Astigmatism is the most common vision problem. It may accompany nearsightedness or farsightedness. It is usually caused by an irregularly shaped cornea, but sometimes it is the result of an irregularly shaped lens. Either type can be corrected by eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.