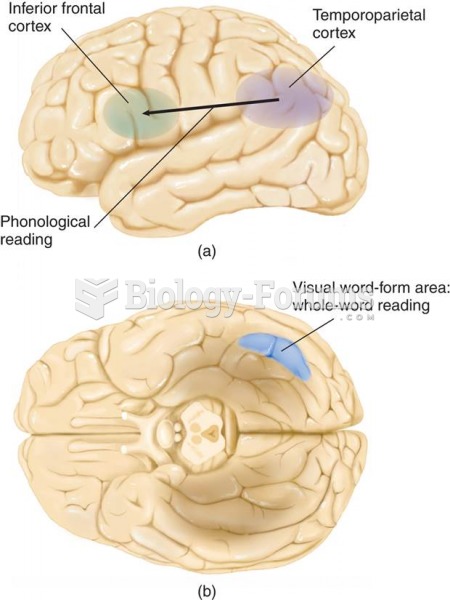
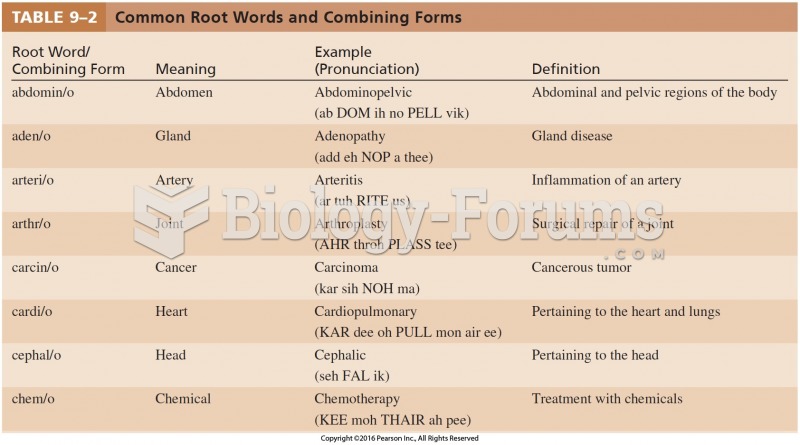
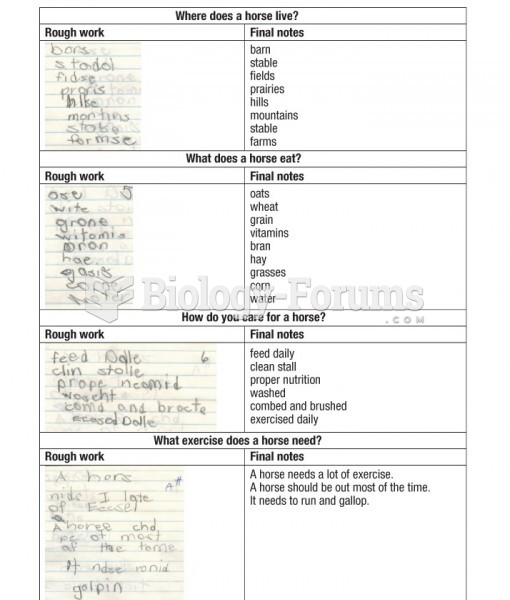
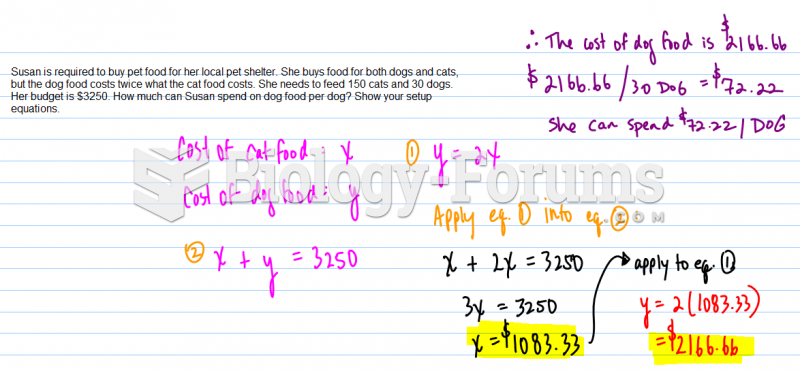|
|
|
The B-complex vitamins and vitamin C are not stored in the body and must be replaced each day.
Immunoglobulin injections may give short-term protection against, or reduce severity of certain diseases. They help people who have an inherited problem making their own antibodies, or those who are having certain types of cancer treatments.
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
Alcohol acts as a diuretic. Eight ounces of water is needed to metabolize just 1 ounce of alcohol.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.