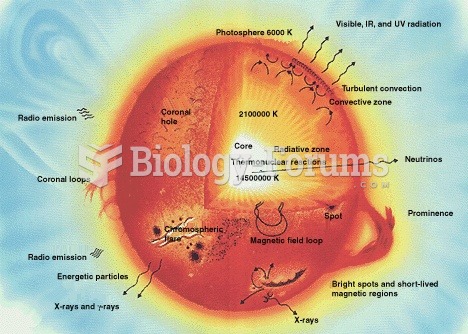
|
|
|
The liver is the only organ that has the ability to regenerate itself after certain types of damage. As much as 25% of the liver can be removed, and it will still regenerate back to its original shape and size. However, the liver cannot regenerate after severe damage caused by alcohol.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.