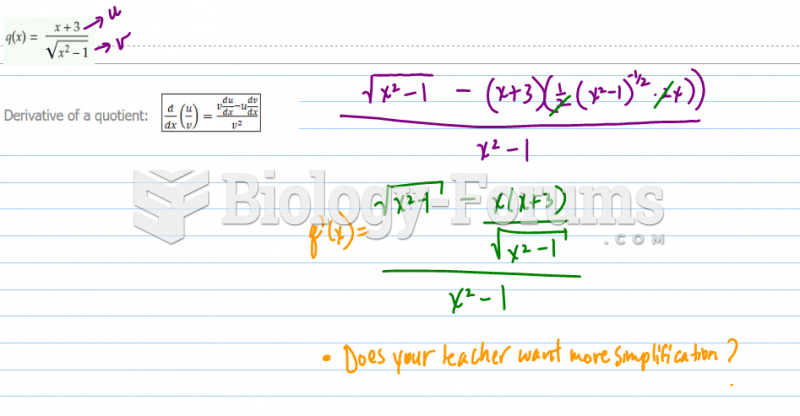
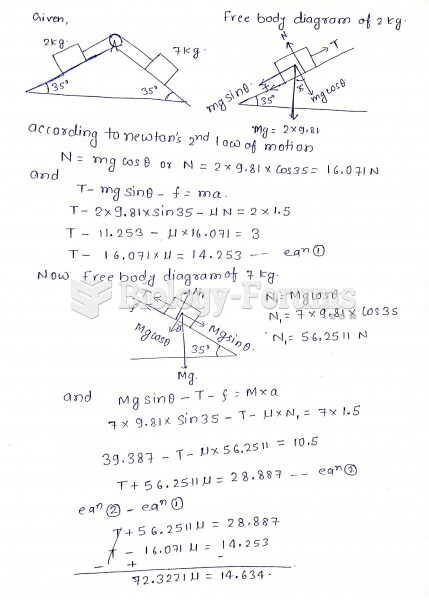
|
|
|
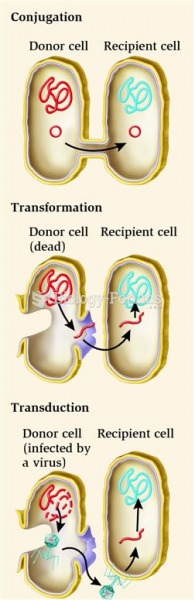
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
More than 4.4billion prescriptions were dispensed within the United States in 2016.
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.