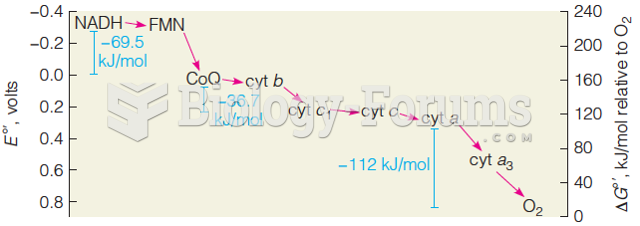This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
Did you know?
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
Did you know?
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
Did you know?
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Did you know?
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.
 Urinalysis. During a simple urinalysis, a stick with colored blocks is dipped into a urine specimen.
Urinalysis. During a simple urinalysis, a stick with colored blocks is dipped into a urine specimen.
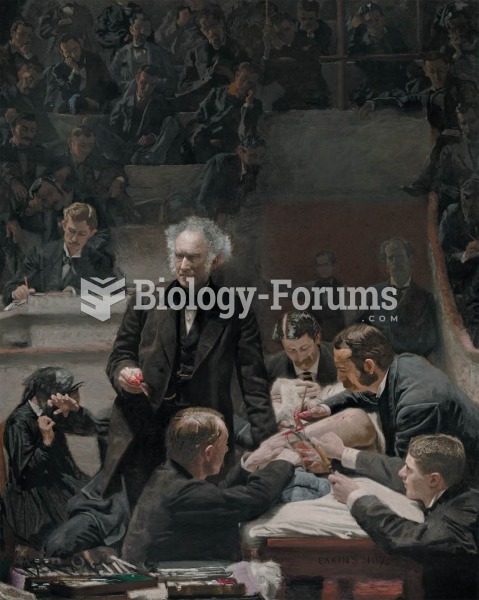 In The Gross Clinic (1875), by Thomas Eakins, Professor Samuel Gross’s team of surgeons cuts through
In The Gross Clinic (1875), by Thomas Eakins, Professor Samuel Gross’s team of surgeons cuts through