|
|
|
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
Liver spots have nothing whatsoever to do with the liver. They are a type of freckles commonly seen in older adults who have been out in the sun without sufficient sunscreen.
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
The most common treatment options for addiction include psychotherapy, support groups, and individual counseling.
Common abbreviations that cause medication errors include U (unit), mg (milligram), QD (every day), SC (subcutaneous), TIW (three times per week), D/C (discharge or discontinue), HS (at bedtime or "hours of sleep"), cc (cubic centimeters), and AU (each ear).
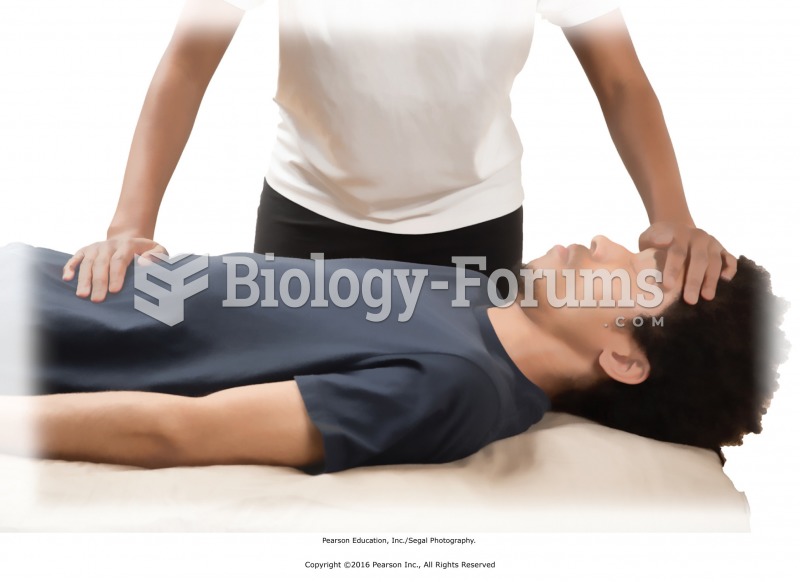
 Finishing techniques for the back of the body. With the recipient fully draped, gently rock the body ...
Finishing techniques for the back of the body. With the recipient fully draped, gently rock the body ...
 Drape recipient for abdominal massage. Tuck drape along sides for secure anchoring. Do not expose ...
Drape recipient for abdominal massage. Tuck drape along sides for secure anchoring. Do not expose ...
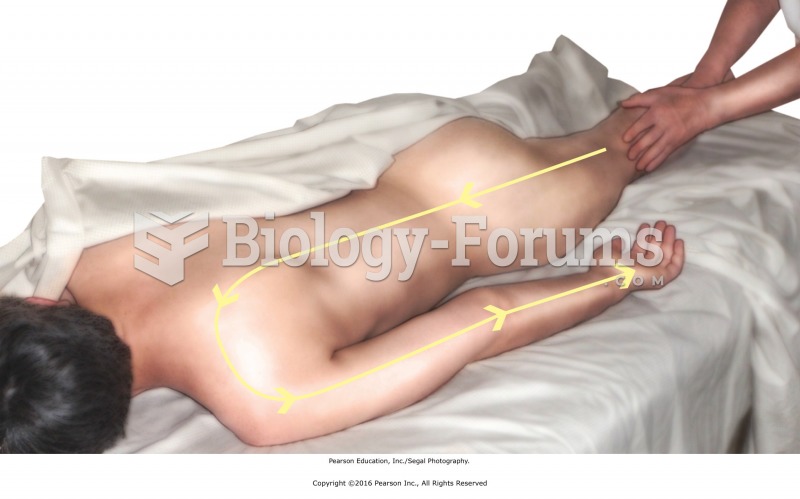 Ayurvedic massage. Long sweeping stroke from foot around shoulder and down the arm, recipient prone.
Ayurvedic massage. Long sweeping stroke from foot around shoulder and down the arm, recipient prone.