|
|
|
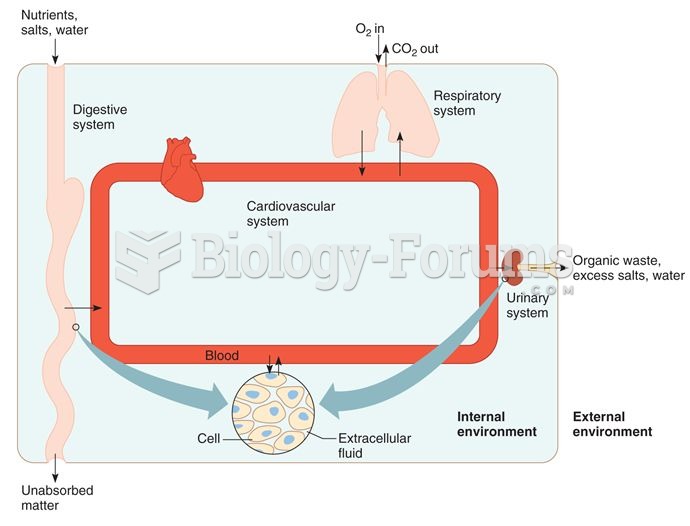
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
Cancer has been around as long as humankind, but only in the second half of the twentieth century did the number of cancer cases explode.
Before a vaccine is licensed in the USA, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviews it for safety and effectiveness. The CDC then reviews all studies again, as well as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Every lot of vaccine is tested before administration to the public, and the FDA regularly inspects vaccine manufacturers' facilities.
Atropine, along with scopolamine and hyoscyamine, is found in the Datura stramonium plant, which gives hallucinogenic effects and is also known as locoweed.
Pope Sylvester II tried to introduce Arabic numbers into Europe between the years 999 and 1003, but their use did not catch on for a few more centuries, and Roman numerals continued to be the primary number system.