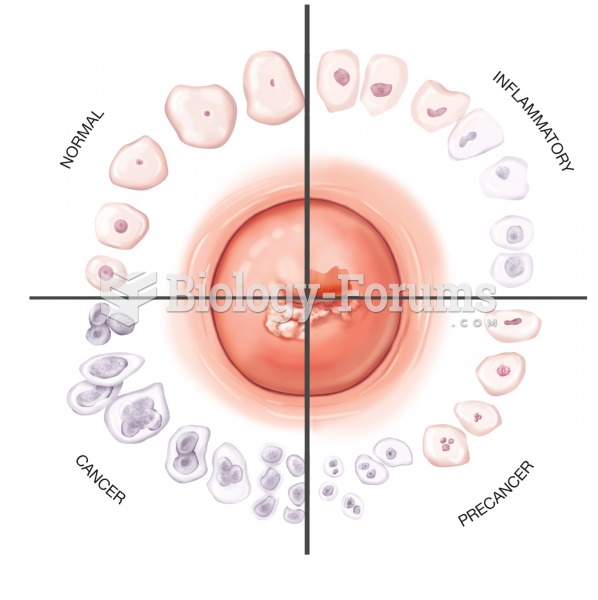
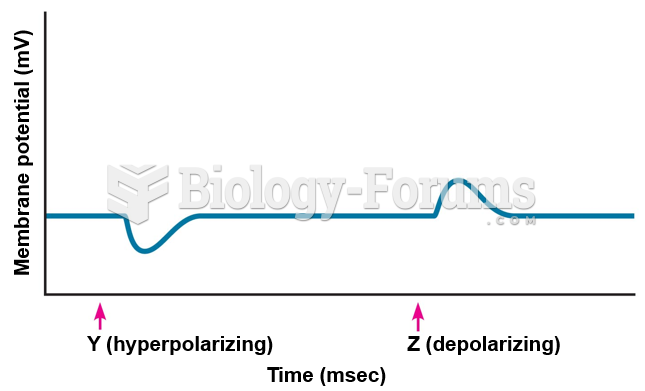
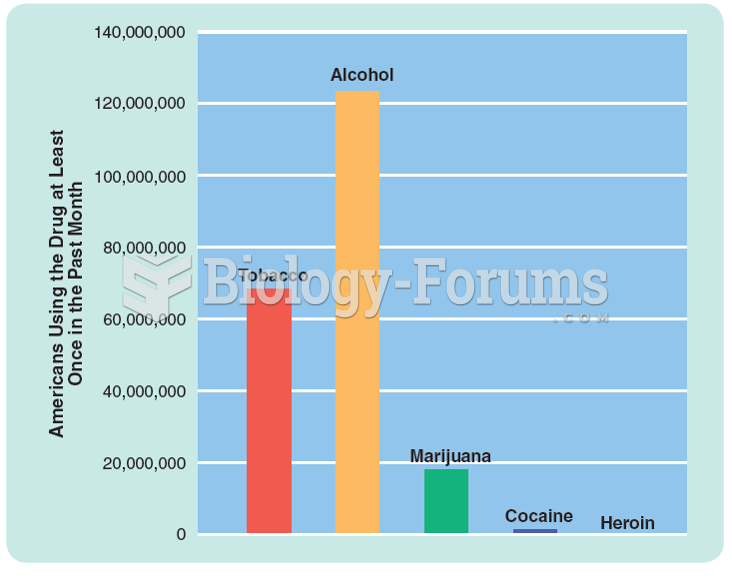
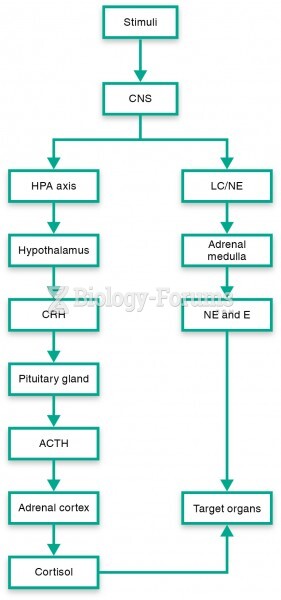
|
|
|
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).
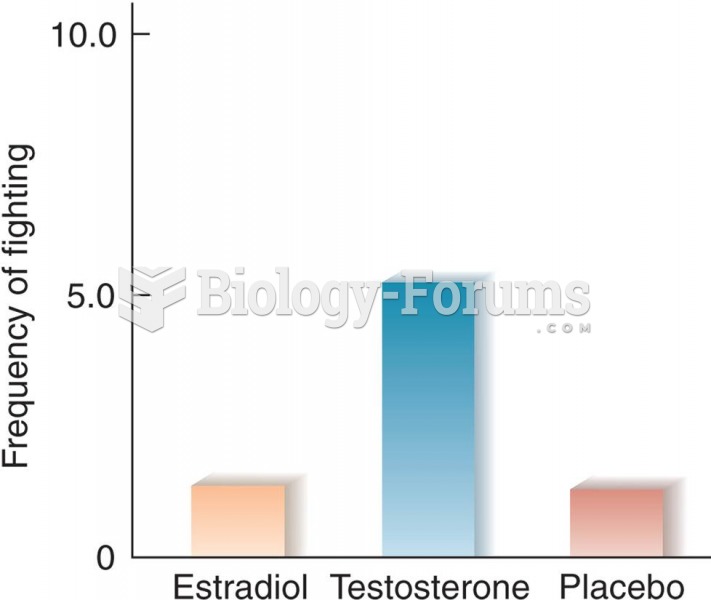 Effects of Estradiol and Testosterone on Interfemale Aggression in Rats (Based on data from van de P
Effects of Estradiol and Testosterone on Interfemale Aggression in Rats (Based on data from van de P
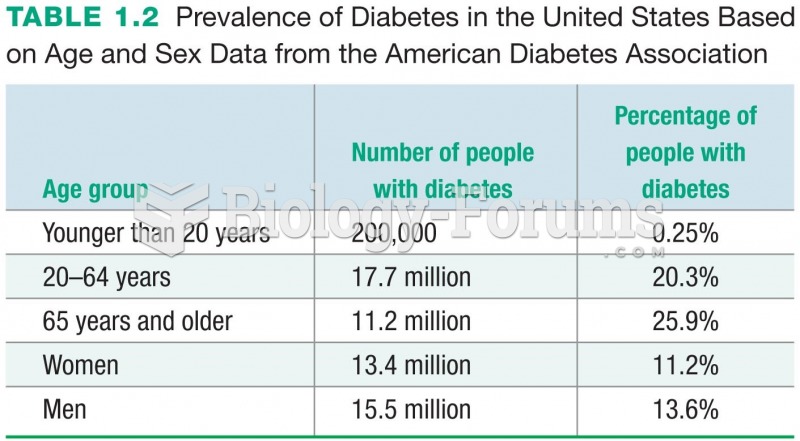 Prevalence of Diabetes in the United States Based on Age and Sex Data from the American Diabetes ...
Prevalence of Diabetes in the United States Based on Age and Sex Data from the American Diabetes ...