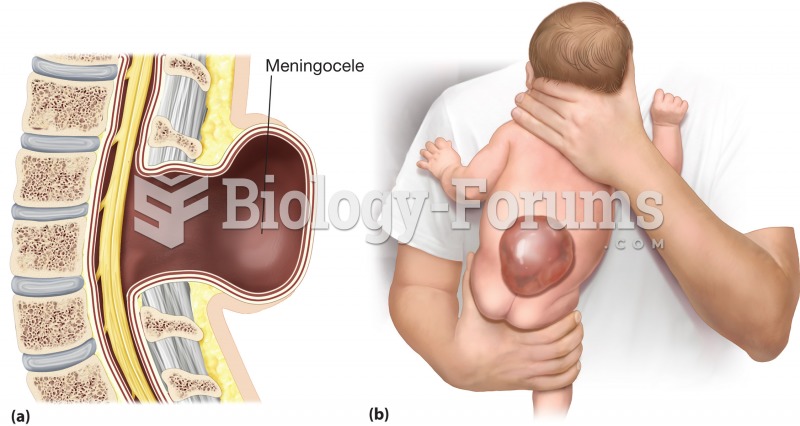
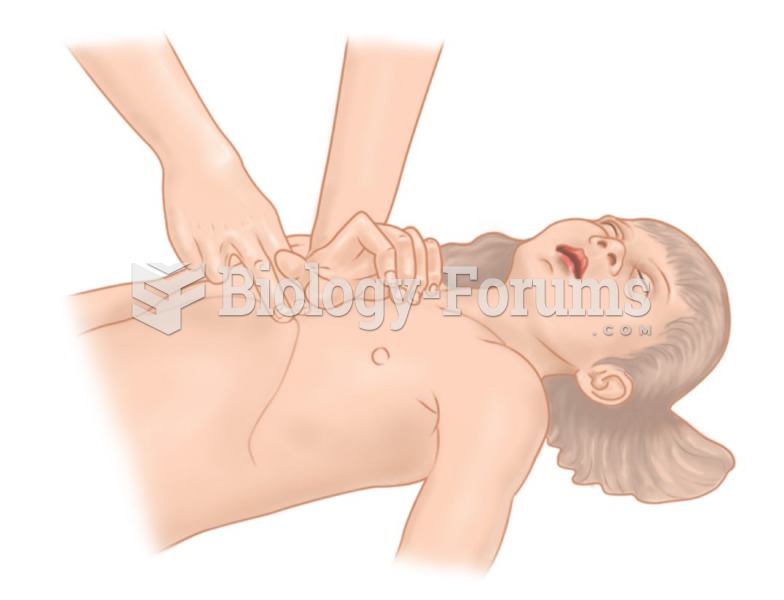
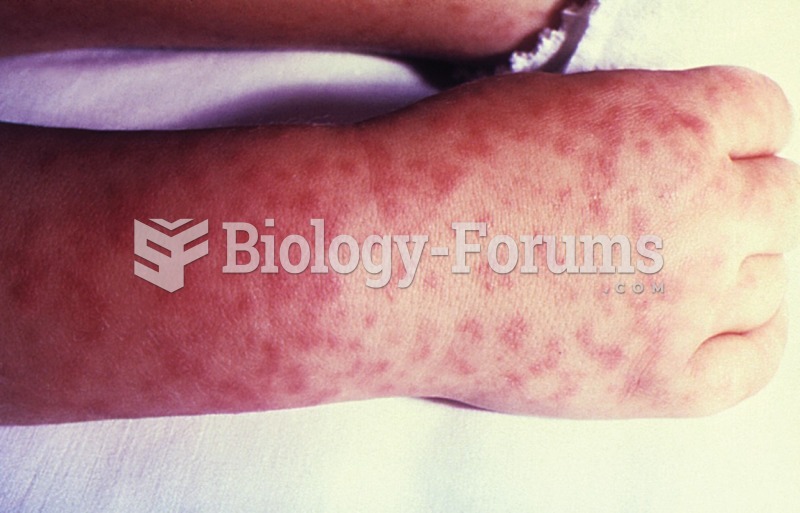
|
|
|
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
People with high total cholesterol have about two times the risk for heart disease as people with ideal levels.
It is believed that humans initially contracted crabs from gorillas about 3 million years ago from either sleeping in gorilla nests or eating the apes.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.