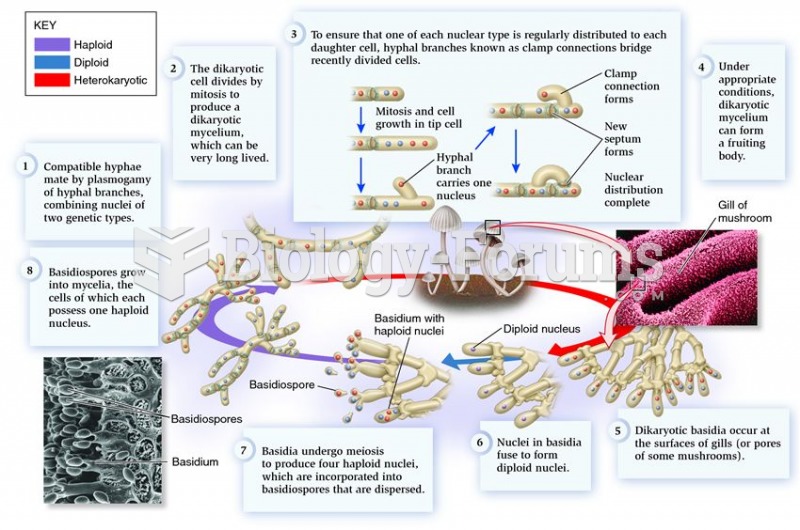
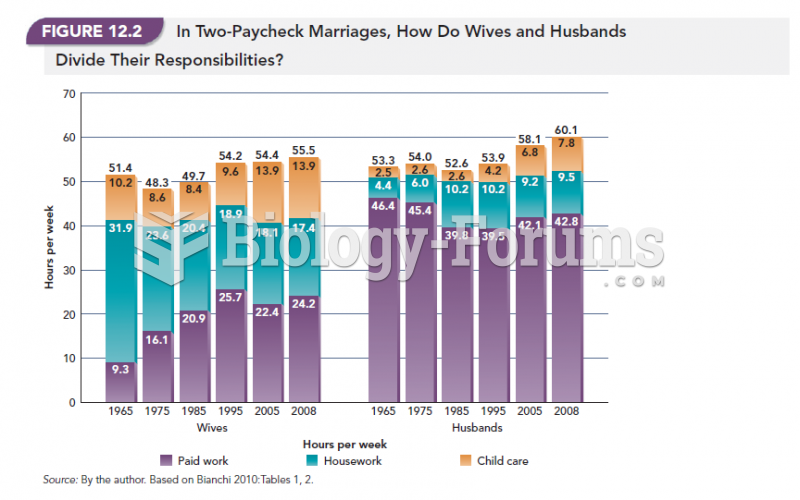
Answer to Question 1
D
Answer to Question 2
Laws regarding marriage and family in the United States have changed considerably
through the decades. Early law had its basis in English common law, which was property
based and patriarchal. Men generally received the most privilege in the law, and women
and children had quite restricted privileges. Women and children were largely viewed as
property of the husband, and the father had quite specific obligations for family support.
The law was designed to make divorce difficult to acquire, women had few rights for
custody of children and alimony, and were largely subordinate to their husband.
As industrialization developed, women acquired more instrumental roles in the workplace,
and consequently they acquired more power and privilege in family relationships. Family
law changed as it adapted to the shifts in status and role, and became more equalitarian in
protecting women's rights. No-fault divorce evolved, women were granted more privileges
for custody of children and child support, inheritance laws guaranteed support obligations
for children, and third party rights of stepparents and relatives were formulated.
Most family law (and change in family law) is in the state domain, with considerable
variation from state to state. Significant change has occurred through the decades, as
change in social behavior has created new legal questions for the courts to resolve. The
areas of greatest current concern revolve around non-traditional partnerships, child support
and adoption, and assisted reproduction. There does not appear to be any major issues that
prevent revision of the laws, and states need to take the initiative. Reform could
accomplish so much, and still be relatively simple.