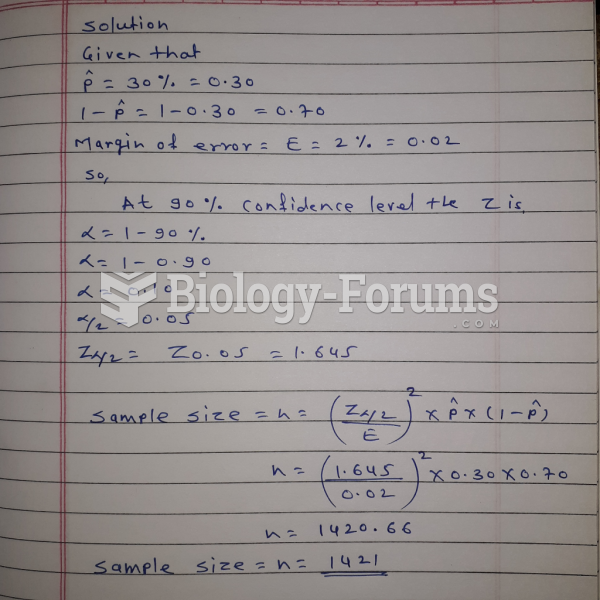
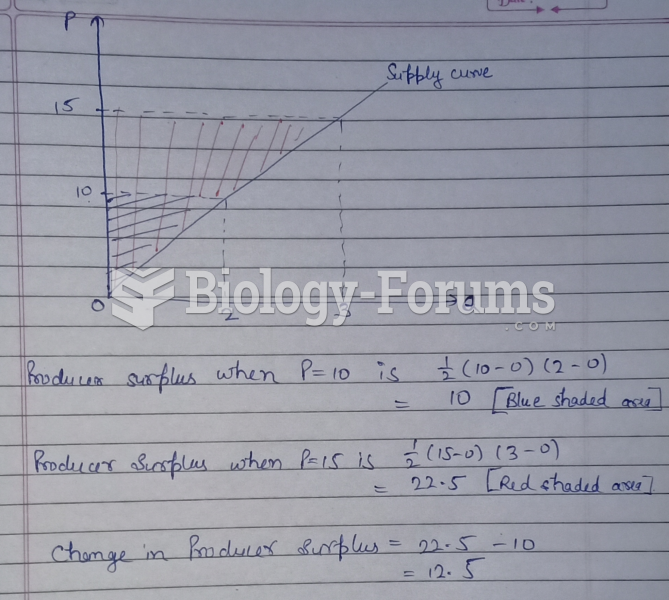
|
|
|
Medication errors are three times higher among children and infants than with adults.
Less than one of every three adults with high LDL cholesterol has the condition under control. Only 48.1% with the condition are being treated for it.
Nearly 31 million adults in America have a total cholesterol level that is more than 240 mg per dL.
A serious new warning has been established for pregnant women against taking ACE inhibitors during pregnancy. In the study, the risk of major birth defects in children whose mothers took ACE inhibitors during the first trimester was nearly three times higher than in children whose mothers didn't take ACE inhibitors. Physicians can prescribe alternative medications for pregnant women who have symptoms of high blood pressure.
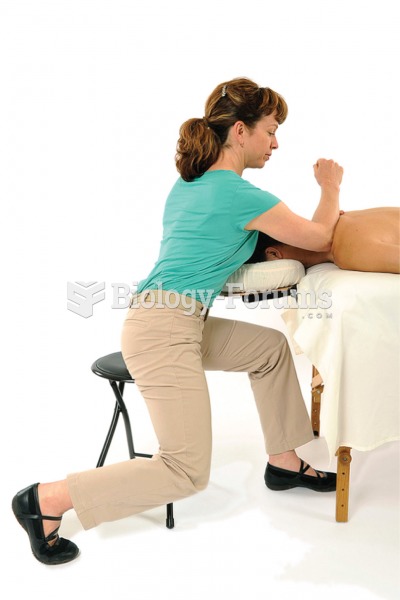
Your skin wrinkles if you stay in the bathtub a long time because the outermost layer of skin (which consists of dead keratin) swells when it absorbs water. It is tightly attached to the skin below it, so it compensates for the increased area by wrinkling. This happens to the hands and feet because they have the thickest layer of dead keratin cells.
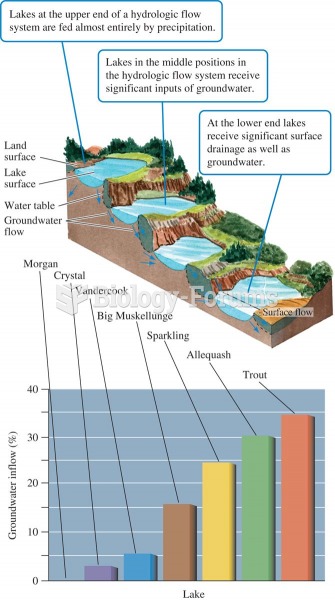 Lake position in the landscape and proportion of water received as groundwater (data from Webster et
Lake position in the landscape and proportion of water received as groundwater (data from Webster et
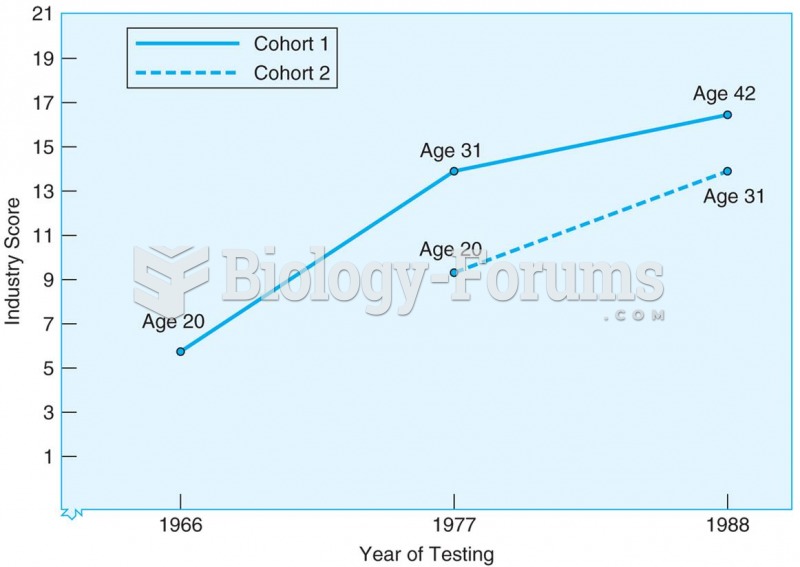 Results from sequential study of two cohorts tested at three ages and at three different points in t
Results from sequential study of two cohorts tested at three ages and at three different points in t