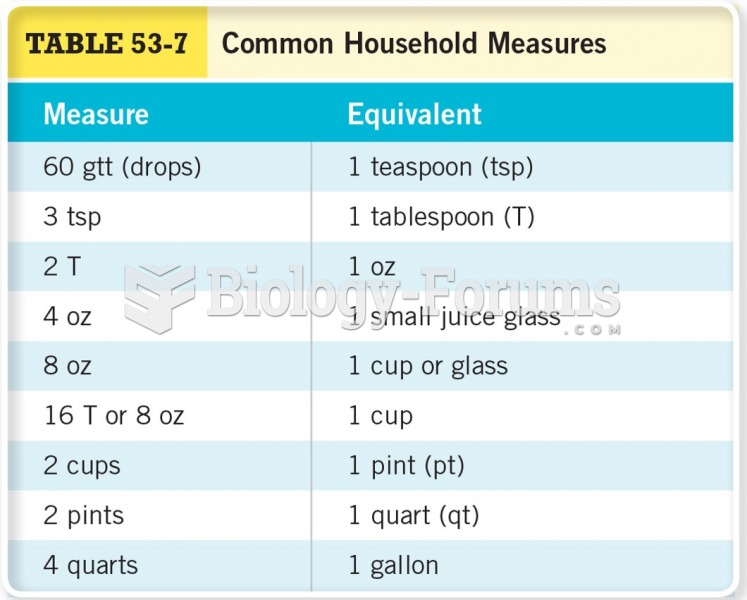
|
|
|
When blood is deoxygenated and flowing back to the heart through the veins, it is dark reddish-blue in color. Blood in the arteries that is oxygenated and flowing out to the body is bright red. Whereas arterial blood comes out in spurts, venous blood flows.
Signs and symptoms that may signify an eye tumor include general blurred vision, bulging eye(s), double vision, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye(s), iris defects, limited ability to move the eyelid(s), limited ability to move the eye(s), pain or discomfort in or around the eyes or eyelids, red or pink eyes, white or cloud spots on the eye(s), colored spots on the eyelid(s), swelling around the eyes, swollen eyelid(s), and general vision loss.
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
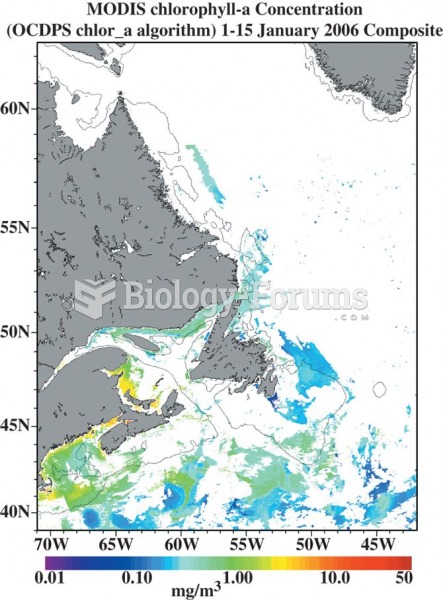 Measures of ocean chlorophyll-a concentrations from part of Atlantic Canada in (a) January 2006, and
Measures of ocean chlorophyll-a concentrations from part of Atlantic Canada in (a) January 2006, and
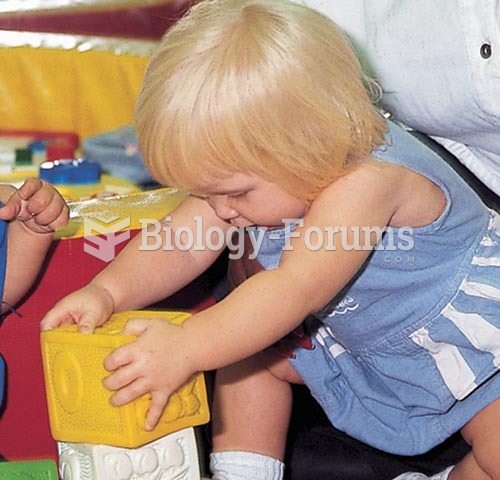 This 11-month old girl demonstrates one of the abilites of a child of this age group - creating a to
This 11-month old girl demonstrates one of the abilites of a child of this age group - creating a to
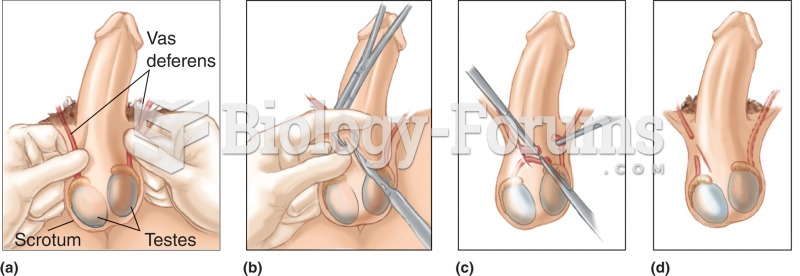 Vasectomy. (a) Vas deferens is located within the spermatic cord on both sides. (b) A small incision
Vasectomy. (a) Vas deferens is located within the spermatic cord on both sides. (b) A small incision