Answer to Question 1
ANS: A, B, E
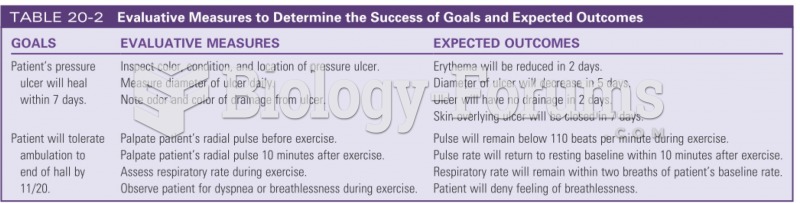
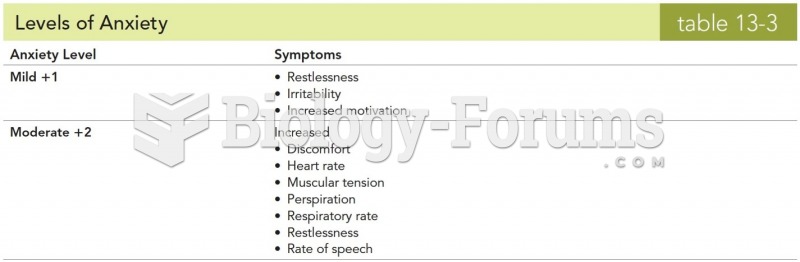
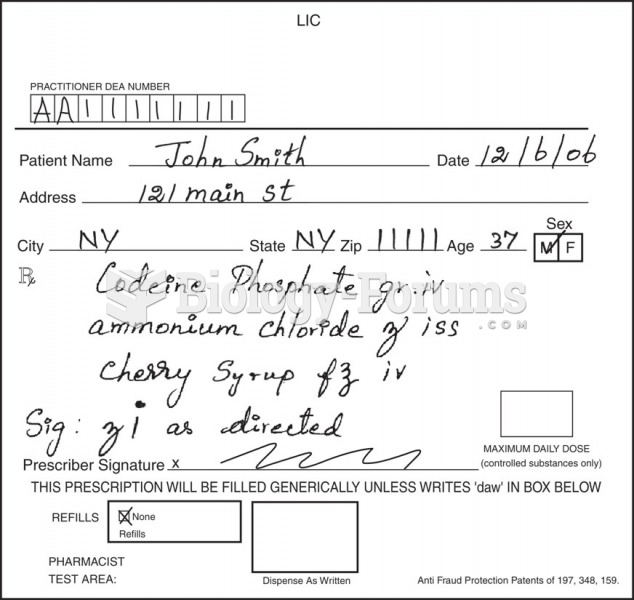
Stability reliability is concerned with the consistency of repeated measures of the same attribute with the use of the same scale or instrument over time. It is usually referred to as test-retest reliability. It reveals random error of measurement. This change in scores could be due to normal random measurement error. If so, the sum of the error (the measured change) for all subjects should be zero, and the means on the two days should be the same. Random error does not influence the mean to be higher or lower but, rather, increases the amount of unexplained variance around the mean. Systematic error is not revealed on test-retest. Test-retest does not measure validity but reliability. On the other hand, test-retest reliability requires the assumption that the factor being measured has not changed between the measurement points. Many of the phenomena studied in nursing, such as hope, coping, pain, and anxiety, do change over short intervals.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: A, B, C, E
Stability reliability is concerned with the consistency of repeated measures of the same attribute with the use of the same scale or instrument over time. It is usually referred to as test-retest reliability. Test-retest may include an additional retest, especially when an unanticipated event has occurred. A third measurement may capture the Hawthorne effect. To capture a complex concept, researchers use the multimethod-multitrait technique, or even a mixed methods design, employing a variety of data collection methods, such as scale, interview, and observation. These techniques allow researchers to measure more dimensions of abstract concepts, and the effect of the systematic error on the composite observed score decreases. Subjects' knowledge of a study could influence their behavior and possibly alter the research outcomes. This threatens the validity or accuracy of the measurements. This change could be due to normal random measurement error. If so, the sum of the error (the measured change) for all subjects should be zero, and the means on the two days should be the same. Random error does not influence the mean to be higher or lower but, rather, increases the amount of unexplained variance around the mean.
On the other hand, test-retest reliability requires the assumption that the factor being measured has not changed between the measurement points. Many of the phenomena studied in nursing, such as hope, coping, pain, and anxiety, do change over short intervals. Perhaps true change has occurred.