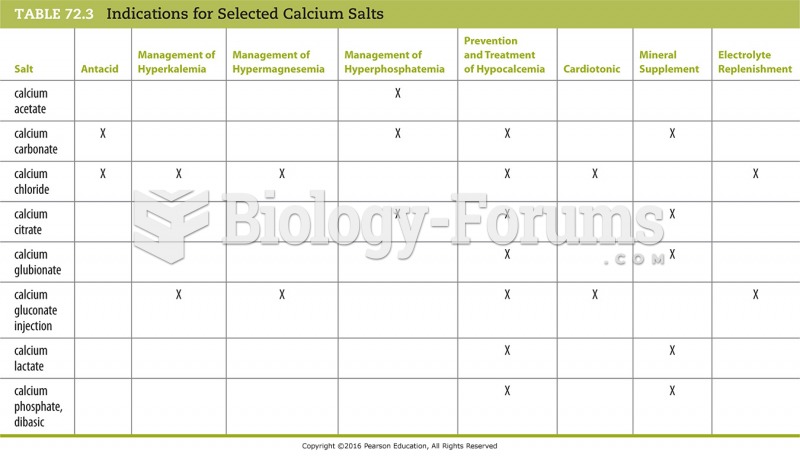
Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Administering both drugs could potentiate AV block in this client.
Rationale 2: Both drugs reduce conduction through the AV node and should be administered with caution to this client.
Rationale 3: Verapamil, a calcium channel blocker, mimics the action of the beta1-adrenergic blocker in blocking conduction through the AV node, and should not be administered to this client. Metoprolol, a beta1-adrenergic blocker, mimics the action of the calcium channel blocker verapamil in blocking conduction through the AV node, and should not be administered to this client.
Rationale 4: Both verapamil and metoprolol block conduction through the AV node, so neither drug should be administered to this client.
Global Rationale: Both drugs reduce conduction through the AV node and should be administered with caution to this client. Administering both drugs could potentiate AV block in this client. Verapamil, a calcium channel blocker, mimics the action of the beta1-adrenergic blocker in blocking conduction through the AV node, and should not be administered to this client. Metoprolol, a beta1-adrenergic blocker, mimics the action of the calcium channel blocker verapamil in blocking conduction through the AV node, and should not be administered to this client. Both verapamil and metoprolol block conduction through the AV node, so neither drug should be administered to this client.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Opening of calcium channels increases intracellular calcium and vascular smooth muscle contraction, raising blood pressure.
Rationale 2: Beta1-adrenergic blockers prevent sympathetic impulse generation that leads to calcium channel opening, but calcium channel blockers work at the level of the calcium ion channel, and do not directly suppress sympathetic impulse generation.
Rationale 3: Beta1-adrenergic blockers cause calcium ion channels to close by preventing sympathetic stimulation of membrane depolarization, and calcium channel blockers cause a change in calcium channel shape that prevents calcium influx into smooth muscle cells. Both mechanisms of drug action decrease intracellular calcium and prevent vascular smooth muscle contraction.
Rationale 4: Neither calcium channel blockers nor beta1-adrenergic blockers affect the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to promote urinary sodium excretion.
Global Rationale: Beta1-adrenergic blockers cause calcium ion channels to close by preventing sympathetic stimulation of membrane depolarization, and calcium channel blockers cause a change in calcium channel shape that prevents calcium influx into smooth muscle cells. Both mechanisms of drug action decrease intracellular calcium and prevent vascular smooth muscle contraction. Opening of calcium channels increases intracellular calcium and vascular smooth muscle contraction, raising blood pressure. Beta1-adrenergic blockers prevent sympathetic impulse generation that leads to calcium channel opening, but calcium channel blockers work at the level of the calcium ion channel, and do not directly suppress sympathetic impulse generation. Neither calcium channel blockers nor beta1-adrenergic blockers affect the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system to promote urinary sodium excretion.