Answer to Question 1
Sample response:
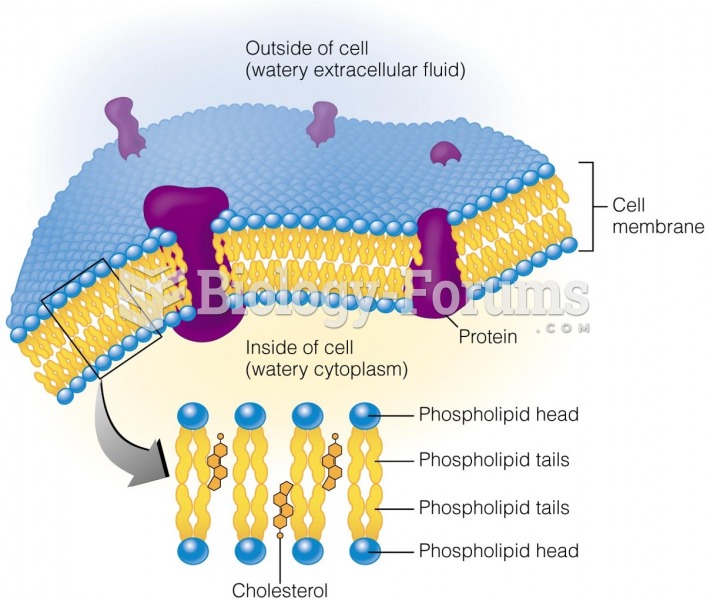
The egg that was released from the ovary is drawn up into the fallopian tube. One sperm cell from the ejaculate must meet and penetrate the egg. Once conception has taken place, this new organism is called a zygote. Over the course of two to four days, it divides and moves down the fallopian tube to the uterus. By the time it arrives in the uterus, it consists of about 90 cells. It is now called a blastocyst. On the sixth or seventh day after fertilization, it implants in the wall of the uterus. The successful attachment is the beginning of pregnancy. Once implantation occurs, the blastocyst is referred to as an embryo.
Answer to Question 2
Sample response:
First trimester
- Month 1. The embryo resembles a tadpole or tiny shrimp; the buds of arms and legs begin to appear; the heart begins to beat; the embryo is about the size of the eraser on a pencil and weighs less than 1 ounce.
- Month 2. The embryo grows to about 1 inch long; distinct fingers and toes appear; the heart muscle has divided into chambers; facial features are visible; the placenta is functioning, bringing nutrients to the embryo and carrying wastes away; the embryo takes on a more human appearance.
- Month 3. The embryo, now called a fetus, grows to about 3 inches in length; fingers and toes have nails; the fetus begins to move in the uterus, but movements cannot usually be felt by the mother; all vital organs and muscles are formed and functioning by the tenth week. The fetus now weighs about 1.2 ounces (the equivalent of a dozen U.S. pennies).
Second trimester
- Month 4. Fetal movement increases and includes kicking, sucking, and swallowing; about 20 tooth buds develop; fingers and toes are more clearly defined; the sex of the fetus may now be determined by observing the growth of the genitals with ultrasound. The fetus grows to 6 or 7 inches long and now weighs around 6 or 7 ounces.
- Month 5. Fetal activity increases further and may even include rolls, flips, and somersaults; the fetus enters a predictable waking-sleeping cycle; the mother will feel frequent, unmistakable movements of the fetus; fetal eyelashes and eyelids appear; growth accelerates to 8 to 10 inches long and weight increases to nearly a pound by the end of the fifth month.
- Month 6. Fetal skin is red and wrinkled and covered with a protective coating called the vernix; the eyes open and close; the fetus's lungs are breathing the amniotic fluid in and out; the fetus is capable of hearing sounds from the outside world; rapid growth continues as the fetus reaches 11 to 14 inches in length and 1.5 to 2 pounds. If born in this month, the baby, though very premature, will have a good chance of survival with specialized intensive care.
Third trimester
- Month 7. The fetus's taste buds have developed, and it may be observed sucking its thumb; muscle tone develops through kicking and stretching; clear responses to external sounds may be observed; layers of fat are forming beneath the skin; internal organs are maturing quickly. If born prematurely at this time, the baby has a high chance of survival and a normal life with proper medical care. The fetus reaches 14 to 16 inches long and about 3 pounds by the end of the seventh month.
- Month 8. The fetus rotates to head-down position; the brain grows quickly; overall growth is now at a rate of a half pound per week; the fetus's kicks and elbow thrusts now become visible from the outside surface of the mother's abdomen; the fetus's internal organs, except for the lungs, are nearly fully developed; the skull bones are flexible and not yet connected to allow them to compress for passage through the birth canal; size is approximately 18 inches long, and weight is 4 to 6 pounds at the end of this month.
- Month 9. The fetal lungs develop fully and are ready to breathe air; the skin typically becomes pink and smooth; the fetus now turns and settles head down, low in the mother's uterus, in preparation for birth; activity decreases, producing fewer noticeable movements; on average, the fetus reaches 18 to 22 inches in length and 6 to 9 pounds as the onset of labor approaches.