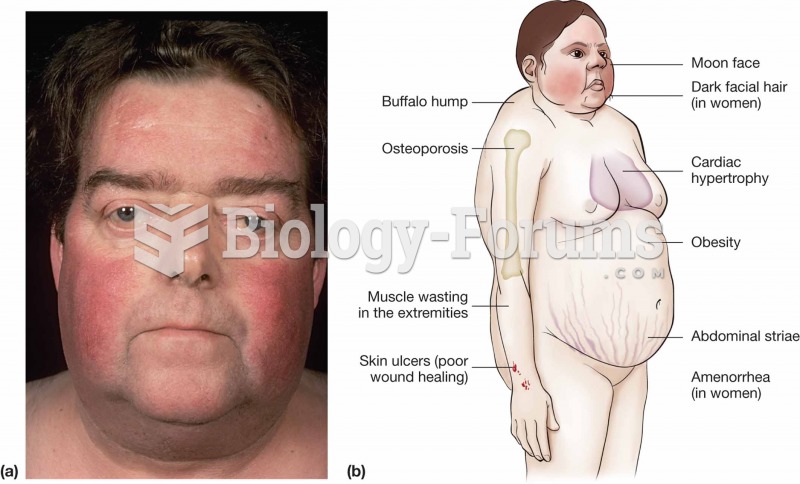
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
More than 150,000 Americans killed by cardiovascular disease are younger than the age of 65 years.
Did you know?
More than 20 million Americans cite use of marijuana within the past 30 days, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). More than 8 million admit to using it almost every day.
Did you know?
More than 34,000 trademarked medication names and more than 10,000 generic medication names are in use in the United States.
Did you know?
Russia has the highest death rate from cardiovascular disease followed by the Ukraine, Romania, Hungary, and Poland.
Did you know?
The modern decimal position system was the invention of the Hindus (around 800 AD), involving the placing of numerals to indicate their value (units, tens, hundreds, and so on).